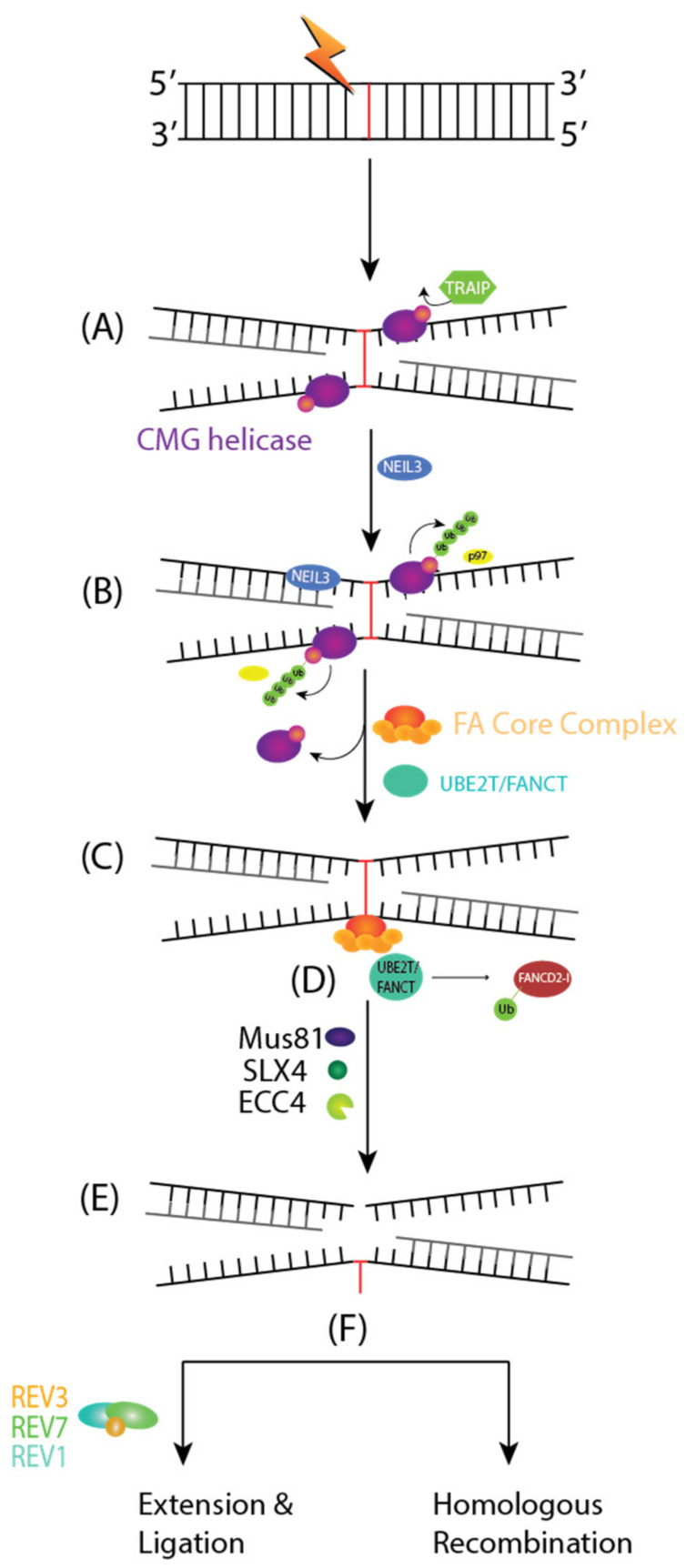
Figure 4.
Fanconi Anemia (FA) Pathway of Interstrand Crosslinks (ICLs). (A) ICLs occurring during the S phase of the cell cycle will converge two replication forks creating an X-shaped structure surrounding it. TRAIP will ubiquitinate CMG helicase to recruit NEIL3 Glycosylase for an incision-dependent unhooking mechanism of ICL resolution. (B) Subsequently, CMG is evicted from the chromatin through long Ub chains and p97, allowing for the approach of both replication forks towards the ICL. This commits the repair to FA pathway-mediated ICL repair. (C) The FA Core Complex is recruited to the chromatin through UHRF1 and FANCM-MHF1-MHF2 complex (not depicted). (D) The FA Core Complex and UBE2T/FANCT E2 conjugating enzymes will monoubiquitinate FANCD2-I. FANCD2-I will recruit Mus81, SLX4, and ERCC4 endonucleases (E) to cleave the DNA strand contiguous to the ICL and generate a DNA adduct and an ICL-derived DSB. (F) The DNA adduct is bypassed by REV1, REV7/FANCV, and REV3 and a DSB will be repaired through HR, respectively.