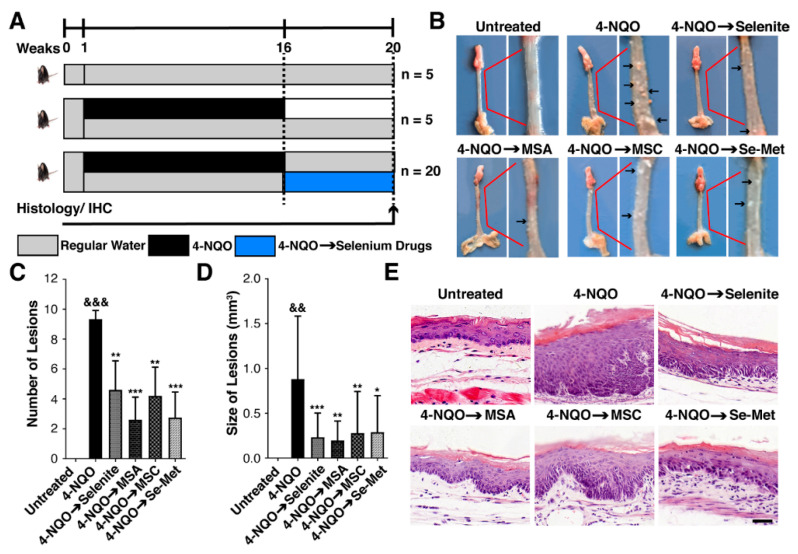
Figure 2.
Selenium impedes ESCC lesions in the 4-NQO mice model. (A) Scheme for the treatment paradigm. C57BL/6 mice were randomized into six groups (n = 5, per group) and fed with water or 4-NQO (100 μg/mL) in drinking water for 16 weeks, after which all mice were given deionized water until week 20. Selenite (0.05 mg/kg), MSA (0.05 mg/kg), MSC (0.1 mg/kg), Se-Met (0.1 mg/kg) were administered via intragastric intubation on Monday, Wednesday, Friday after 16 weeks of 4-NQO exposure for 4 weeks. (4-NQO → Se compounds; shaded in blue). The histopathological assessment and immunohistochemistry of esophageal tissues were performed after 20 weeks: (B) Representative images of esophageal lesions for each treatment group. (C) Columns represent the number of esophageal lesions for each treatment group. (D) Columns represent the size of esophageal lesions for each treatment group. (E) Histological analysis of mice’s normal esophagus and ESCC esophagus for each treatment group (magnification, x400; scale bar = 40 μm). Differences are significant at (&&& p < 0.001, && p < 0.01 vs. untreated group, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. 4-NQO group). The difference with p ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.