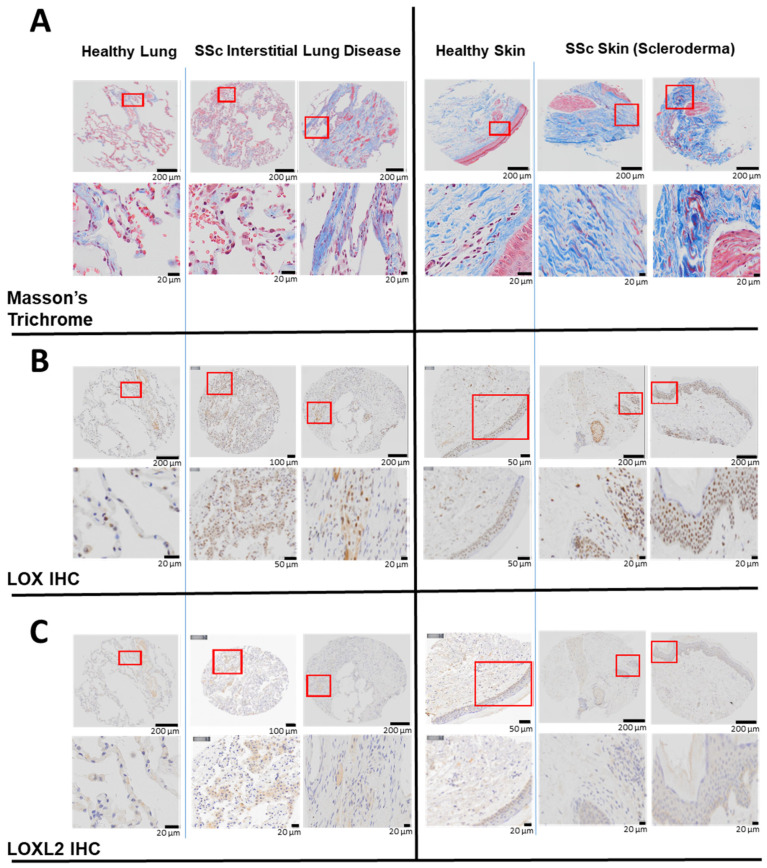
Figure 1.
Elevated LOX and LOXL2 and collagen expression in the lung and skin of human patients with SSc. In lung tissues, LOX and LOXL2 was mainly expressed by macrophages and to a lesser extent by the pneumocytes, and endothelial cells of the lung vessels. In skin, LOX and LOXL2 was mostly expressed by the keratinocytes and epithelial cells within the sebaceous glands and the hair follicles. Positive macrophages and fibroblasts can be seen as well. LOX can be seen highly expressed in the nucleus and cytoplasm in comparison to a weaker signal of LOXL2 and more in the cytoplasm than the nucleus. (A) Masson’s Trichrome staining revealed higher expression of collagen in the lung biopsies from two patients with interstitial lung disease and SSc compared to a healthy human subject, and higher collagen expression in the skin biopsies from a separate group of two patients with scleroderma compared to normal skin from a healthy subject. (B) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining using a specific primary antibody against human native LOX revealed higher expression of LOX in the above lung and skin biopsies compared to the respective healthy subjects. (C) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining using a specific primary antibody against human native LOXL2 revealed higher LOXL2 expression in the lung biopsies from above SSc patients compared to a healthy human subject. LOXL2 expression in the skin is minimal in both the SSc patients and the healthy human subject.