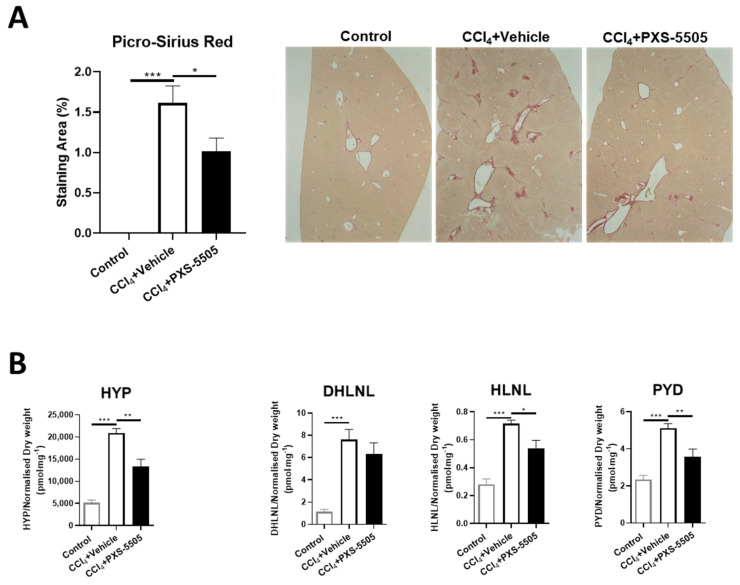
Figure 7.
The effect of PXS-5505 treatment on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis and collagen crosslinks in mouse lung. (A) Representative images of liver stained with Picro-Sirius red, differentiating collagen (red) from hepatocytes (yellow) with quantification of the staining area, showing significantly elevated percentage of collagen deposited area in the mice administered with CCl4 compared to the normal mice, and the fibrotic area reduced in the CCl4 group subjected to PXS-5505 treatment compared to the vehicle treated group. (B) CCl4 administration elevated the expression of hydroxyproline (HYP), immature [dihydroxy-lysinonorleucine (DHLNL) and hydroxylysinonorleucine (HLNL)] and mature [pyridinoline (PYD)] collagen crosslinks in the mouse liver; PXS-5505 treatment ameliorated these elevated markers induced by CCl4. (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 between the indicated groups).