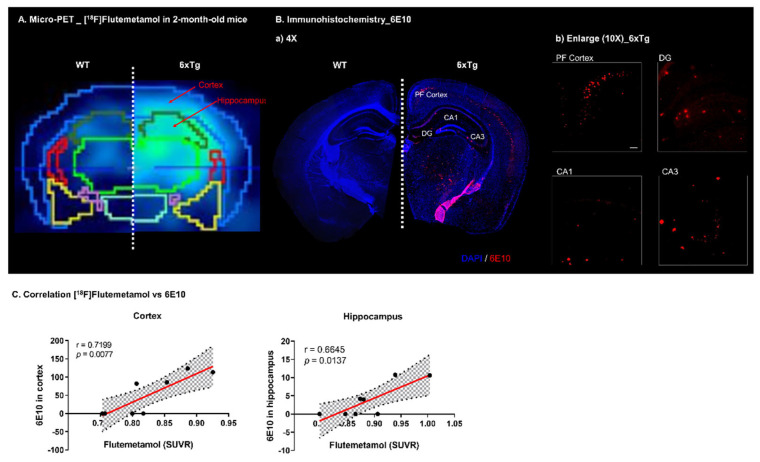
Figure 2.
Representative images of [18F]Flutemetamol and 6E10 immunostained image in brain. (A) The [18F]Flutemetamol intensity of 2-month-old 6 × Tg mice increases in the cortex and hippocampus compared to that in WT mice. (B) Brain tissues of 2-month-old 6 × Tg and WT mice were immunostained with 6E10 antibody and counterstained with DAPI. Representative slices are shown for (a) WT and 6 × Tg mice brain (4× magnification) and (b) cortex (PF) and hippocampus (DG, CA1, and CA3) regions of 6 × Tg mice brain (10× magnification) (all scale bars = 100 μm). 6E10 stained Aβ deposits are shown in the cortex and in the hippocampus of 6 × Tg mice brain. (C) The correlation between [18F]Flutemetamol uptake and relative abundance of 6E10-stained β-amyloid deposits were assessed in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of 6 × Tg mice by the nonparametric Spearman’s rank correlation test. Graphs show regression lines with 95% confidence intervals. [18F]Flutemetamol uptake significantly correlates with the relative abundance of 6E10-stained Aβ deposits both in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of 6 × Tg mice.