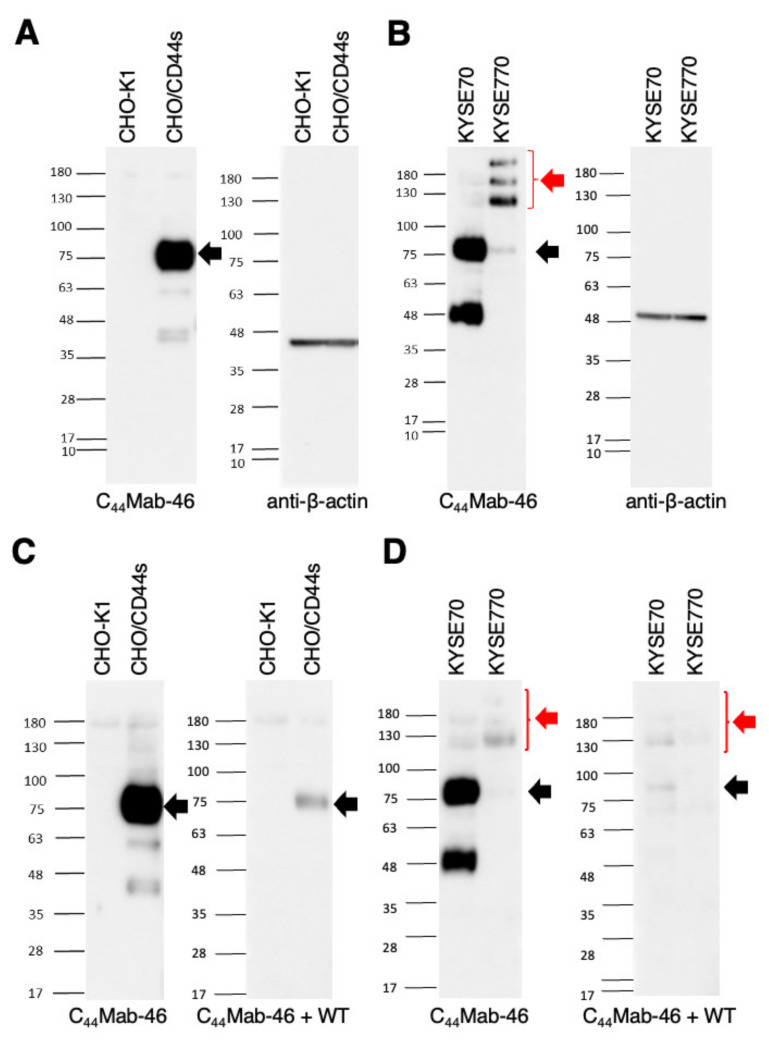
Figure 4.
Western blotting by C44Mab−46. (A) Cell lysates of CHO−K1 and CHO/CD44s (10 µg) were electrophoresed and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes. The membranes were incubated with 1 µg/mL of C44Mab−46 and 1 µg/mL of anti−β−actin and subsequently with peroxidase−conjugated anti−mouse immunoglobulins. (B) Cell lysates of KYSE70 and KYSE770 (10 µg) were electrophoresed and transferred onto PVDF membranes. The membranes were incubated with 1 µg/mL of C44Mab−46 and 1 µg/mL of anti−β−actin and subsequently with peroxidase−conjugated anti−mouse immunoglobulins. (C) Cell lysates of CHO−K1 and CHO/CD44s (10 µg) were electrophoresed and transferred onto PVDF membranes. The membranes were incubated with 1 µg/mL of C44Mab−46 and C44Mab−46 (1 μg/mL) plus the CD44 peptide (10 μg/mL, WT), and subsequently with peroxidase−conjugated anti−mouse immunoglobulins. (D) Cell lysates of KYSE70 and KYSE770 (10 µg) were electrophoresed and transferred onto PVDF membranes. The membranes were incubated with 1 µg/mL of C44Mab−46 and C44Mab−46 (1 μg/mL) plus the CD44 peptide (10 μg/mL, WT), and subsequently with peroxidase−conjugated anti−mouse immunoglobulins. Black arrows indicate the predicted size of CD44s (~85 kDa). The red arrow indicates the CD44 variants.