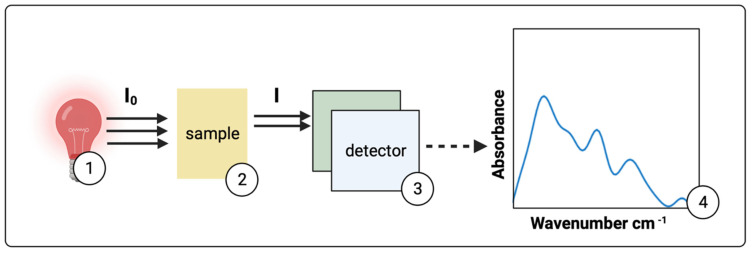
Figure 6.
Basic principles of infrared spectroscopy. (1) Incident broadband infrared light (I0) upon a (2) sample leads to vibrational modes of a molecule. Consequently, specific amounts of energy from the incident light are absorbed. This decreases the subsequently measured infrared light (I) by the detector (3). Data are then acquired for interpretation in the form of a spectrum expressed as absorbance versus wavenumbers in cm−1 (4).