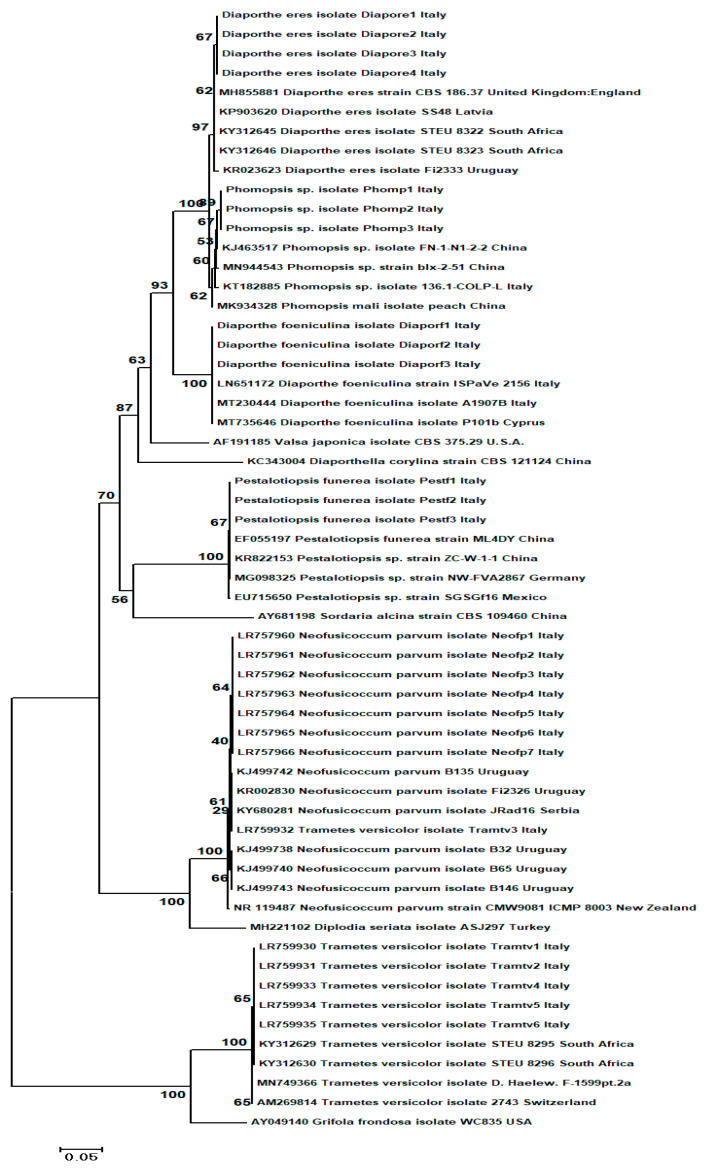
Figure 2.
Molecular phylogenetic tree obtained through the neighbor-joining (NJ) method, based on the 58 ITS region sequences data (658 bp) from fungal isolates in the present study and published sequences. Five fungal species (Diaporthella corylina, Valsa japonica, Sordaria alcina, Grifola fondosa and Diplodia seriata) were used as outgroups in the analysis. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 1.38532669 is shown. The confidence probability estimated using the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Tajima–Nei method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions/site. Scientific names of the fungi along with collection place, isolate abbreviation and GenBank AC number are shown in the trees.