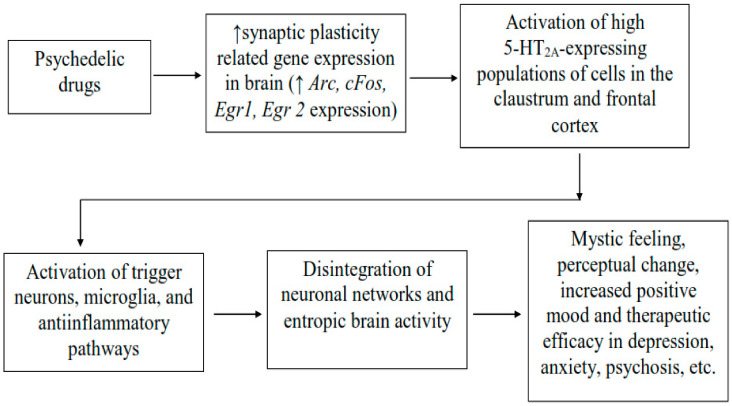
Figure 1.
Neurobiological mechanisms of action of psychedelic drugs beside 5HT2A agonism. Psychedelic drugs mediate increase expression of gene relating to synaptic plasticity in the brain initiating downstream neuronal signaling leading to the activation of neurones showing high expression of 5-HT2A receptors in the brain regions such as claustrum and frontal cortex, and which underlie changes in the cortical network and entropic brain activity using psychedelics. The changes in brain activity may lead to the subjective psychedelic experience such as mystic feeling, perceptual changes, increase positive mood and therapeutic efficacy in depression, psychosis, etc. Arc: activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein; Egr1 and Egr2: early growth response protein 1 and 2; cFos: a marker of neuronal activation [56].