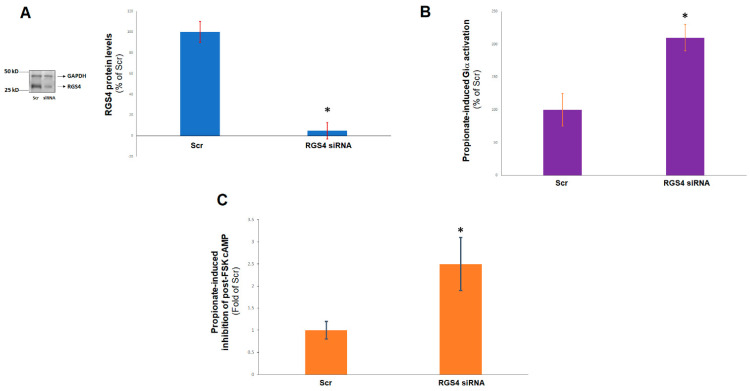
Figure 1.
RGS4 and FFAR3-dependent Gi/o protein activation in cardiac myocytes. (A) Immunoblotting for RGS4 to confirm the efficiency of the siRNA-mediated knockdown of RGS4 in H9c2 cells at 48 hrs post-siRNA transfection. A representative blot, including for glyceraldehyde 3′-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a loading control, is shown on the left, and the % protein reduction, based on densitometric analysis of 4 independent experiments, is shown on the right. Scr: Scrambled siRNA (control); *, p < 0.05; n = 4 independent experiments per condition. (B) A 1 mM propionic acid-induced Giα activation in control (scrambled siRNA-transfected, Scr), or in RGS4-depleted (RGS4 siRNA) H9c2 cells. *, p < 0.05; n = 4 independent experiments. (C) A 1 mM propionic acid-mediated inhibition of 10 μM forskolin (FSK)-induced cAMP accumulation in the same cells, expressed as a % of the inhibition observed in the control (Scr) H9c2 cardiac cells. Forskolin alone induced similar levels of cAMP accumulation in both cell clones (data not shown). *, p < 0.05; n = 4 independent experiments.