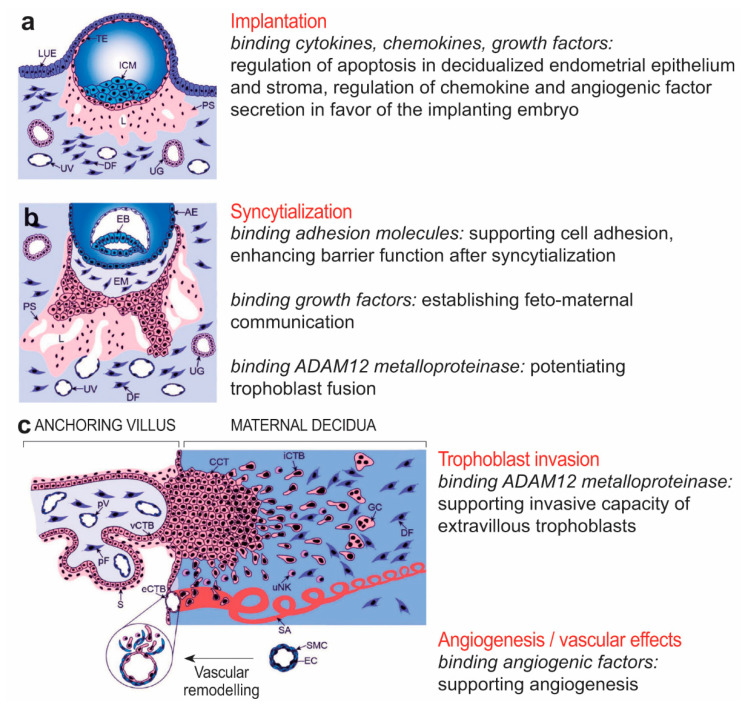
Figure 7.
Physiological aspects of syndecan-1 at the maternal-fetal interface. The figure represents multiple roles of syndecan-1 in implantation, angiogenesis, maternal-fetal immune tolerance, and trophoblast invasion. (a) Embryo implantation. (b) Formation of primary villi by proliferative cytotrophoblasts and syncytialization. (c) Formation of tertiary villi, placental angiogenesis, extravillous trophoblast invasion, and spiral artery remodeling. Amniotic epithelium, AE; cell column trophoblast, CCT; dendritic cell, DC; decidual fibroblast, DF; embryoblast, EB; endothelial cell, EC; extracellular matrix, ECM; extraembryonic mesoderm, EM; endovascular cytotrophoblast, eCTB; giant cell, GC; inner cell mass, ICM; interstitial cytotrophoblast, iCTB; luminal uterine epithelium, LUE; lacunae, L; matrix metalloproteinase, MMP; natural killer, NK; placental fibroblast, pF; primitive syncytium, PS; placental vessel, pV; spiral artery, SA; syncytium, S; smooth muscle cell, SMC; trophectoderm, TE; uterine gland, UG; uterine NK cell, uNK; uterine vessel, UV; villous cytotrophoblast, vCTB. Cartoons are adapted from Knöfler and Pollheimer [103] under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.