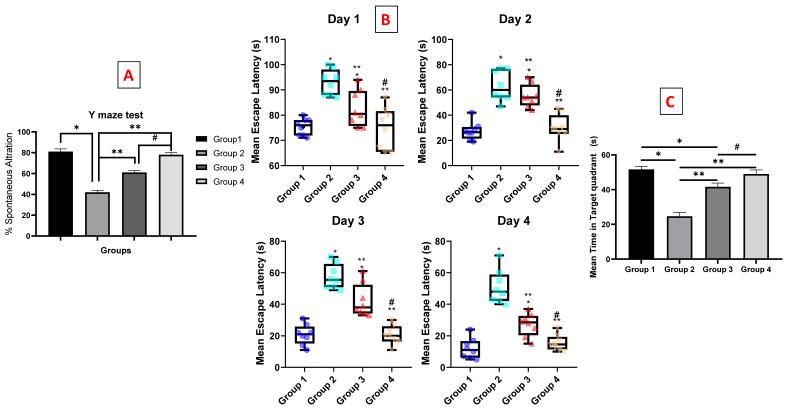
Figure 4.
Behavioral tests on effect of luteolin-chitosomes on ICV-STZ mouse model. Animals were divided into 4 groups, eight animals in each group (n = 8), the first one was the normal control group. The second group was the positive control group that received STZ (3 mg/kg, ICV). The last two groups were all ICV-injected, first with STZ (3 mg/kg) followed by intranasal administration of luteolin suspension (50 mg/kg, every day for 21 days) and luteolin-loaded chitosomes (50 mg/kg, i.n. for 21 days) respectively. (A) Y-maze test that measured the percentage of spontaneous alternation, (B) box and whisker plots of mean escape latency (MEL), and (C) mean time in target quadrant. Statistical analyses for the Morris water maze test (escape latency) were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA. The data that were not included in repeated measures were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. Each value was expressed as mean ± SD. *: Statistically significant different from the normal group at p < 0.05, **: Statistically significant different from the positive control group (STZ, 3 mg/kg) at p < 0.05. #: Statistically significant different from the luteolin suspension group (50 mg/kg).