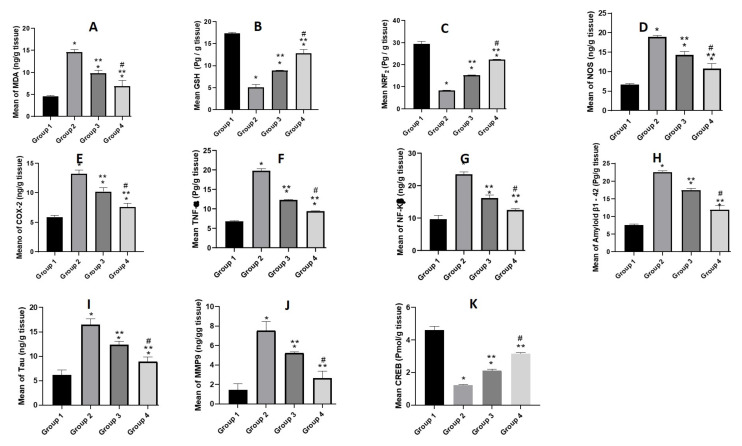
Figure 10.
Biochemical assay where animals under investigation were divided into 4 groups; the first one was the normal control group. The second group was the positive control model group that received STZ (3 mg/kg, ICV). The last two groups were all ICV-injected first with STZ (3 mg/kg) followed by i.n. injection with luteolin suspension (50 mg/kg, for 21 days), and luteolin loaded chitosomes (50 mg/kg, i.n. for 21 days), respectively. The brains of the animals (n = 8) in each group were homogenized then centrifuged, and supernatants were used in the oxidative stress parameters assay of (A) mean MDA concentration, (B) GSH level and (C) NRF2 level. The proinflammatory mediators’ assay of (D) mean NOS level, (E) COX-2 level (F) TNF-α level, and (G) NF-Kβ levels. The amyloidogenicity and tauopathy of (H) mean of Amyloid β1-42 level, and (I) Tau level. Finally, (J) MMP9, and (K) CREB level. Statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test, whereby each value was expressed as mean ± SD. * Statistically significant difference from the normal group (p < 0.05); ** statistically significant difference from the STZ model group, (p < 0.05); # statistically significant difference from the LUT susp group 50 mg/kg (p < 0.05).