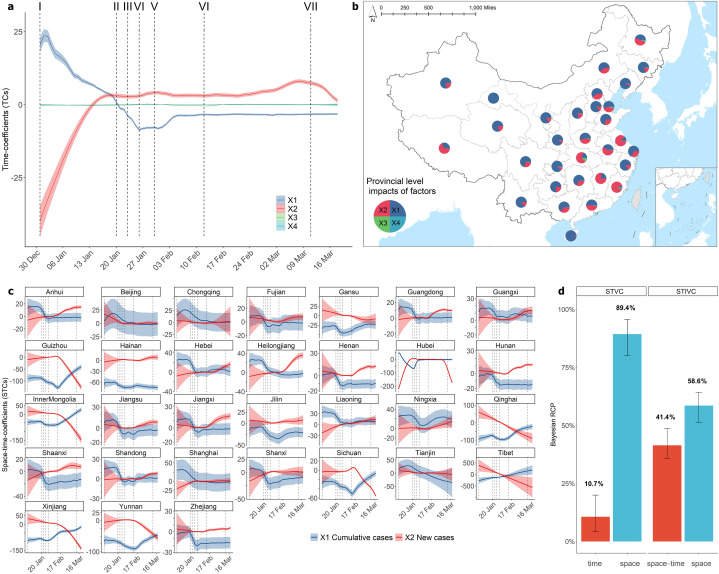
Fig. 4.
Temporal heterogeneous associations between regional public attention and daily varying factors at the national and provincial levels in China. a, National-level impacts of daily varying factors (X1-X4) on public attention using parameter time-coefficients (TCs) with 95% CIs. b, Provincial-level average impacts of factors (X1-X4) on public attention mapped using the average effect of space–time-coefficients (STCs). c, Provincial-level public risk perception: temporally varying associations (STCs with 95% CIs) between daily public attention and COVID-19 cases (X1 and X2) demonstrated large disparities across 31 provinces in China. d, Bayesian RCP index with 95% CIs in STVC and STIVC models: differences in contribution percentages of factors at the time (national), space–time (provincial level) and space (city level) scales. Only factors X1 through X4 have time-dimension variations, namely, X1 cumulative cases, X2 new cases, X3 inflow population, and X4 outflow population. Vertical dashed lines represent those important events (I-VII) regarding China's COVID-19 development in terms of influencing collective public attention (Fig. 2a). Here, the STIVC model refers to the standard model with an SSH-type spatiotemporal interaction.