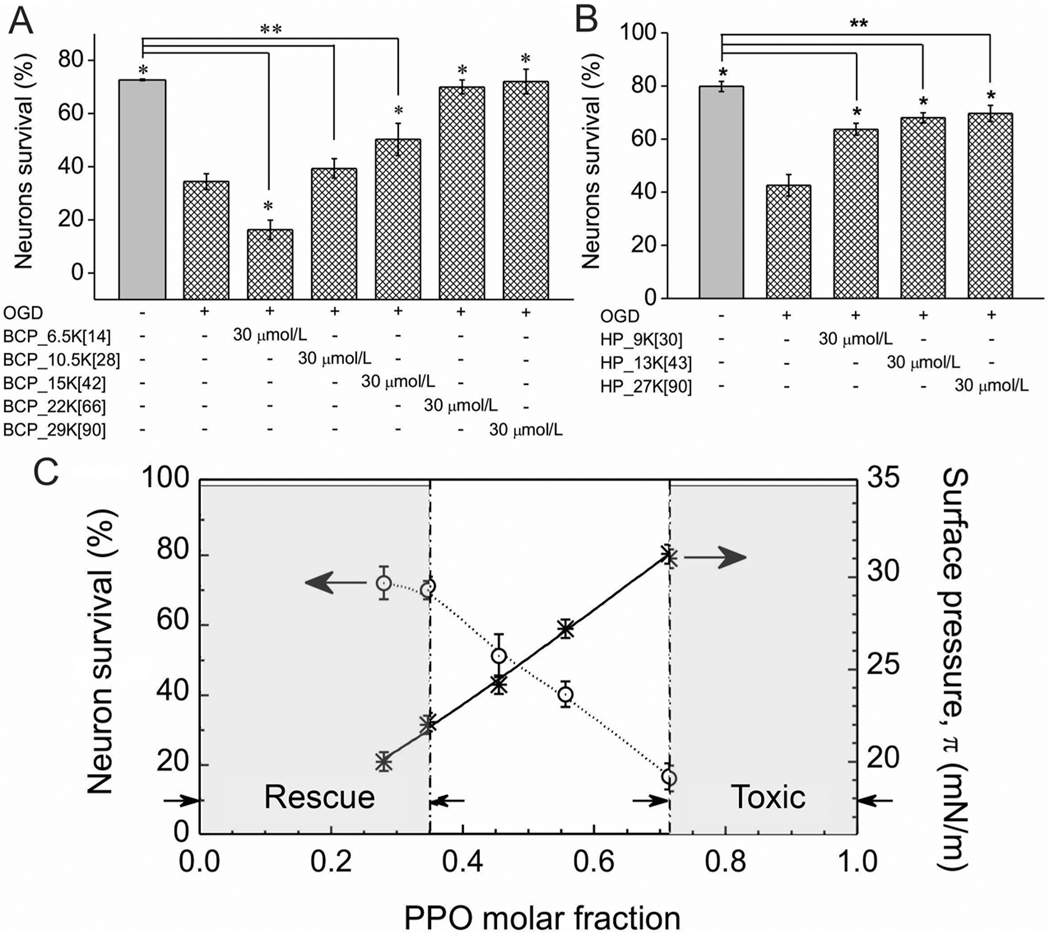
Figure 3.
Effects of polyMPC-PPO-polyMPC triblock copolymers and polyMPC homopolymers on neuronal survival. (A) Quantification of the effects of polyMPC-PPO-polyMPC on cultured embryonic rat hippocampal neuron survival following OGD at 37 °C. (B) Quantification of the effects of molecular weight of polyMPC homopolymer on cultured embryonic rat hippocampal neuron survival following OGD at 37 °C. * p < 0.05 as compared to OGD (+); ** p < 0.05 as compared to OGD (−). (C) The correlation among the Gibbs adsorption surface pressure, π, neuronal survival, and the molar fraction of PPO for polyMPC-PPO-polyMPC at a polymer concentration of 30 μmol/L. PolyMPC-PPO-polyMPC with fPPO < 0.35 is expected to be a membrane-targeting cellular rescue agent; polyMPC-PPO-polyMPC with fPPO > 0.71 is expected to be toxic to neurons.