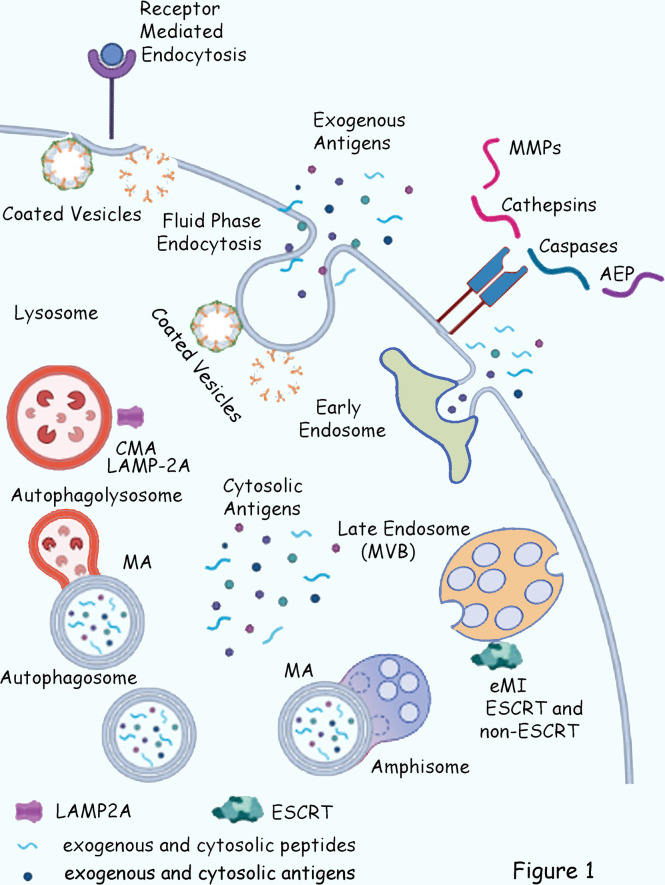
Figure 1.
Schematic of the cytosolic and exogenous pathways for antigen delivery to MHC II compartments. Exogenous antigens are acquired through fluid phase endocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cytosolic proteins enter MHC II compartments through Macroautophagy (MA), upon fusion of the Autophagosomes with Lysosomes (Autophagolysosome) or with Late Endosomes (Amphisome); Endosomal Microautophagy (eMI, ESCRT-dependent and independent), and LAMP2A-mediated chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). Additional antigen-acquisition routes include preprocessed cytosolic proteasome-generated peptides, as well as acquisition of extracellular peptides present in biological fluids loaded on plasma membrane and early-endosomes recycling MHC-II molecules. As such, MHC-II-eluted self-peptides derived from a variety of processing pathways including Cathepsins, Caspases and other endopeptidase such as asparagine endopeptidase (AEP), and matrix metalloproteases (MMPs), among many others.