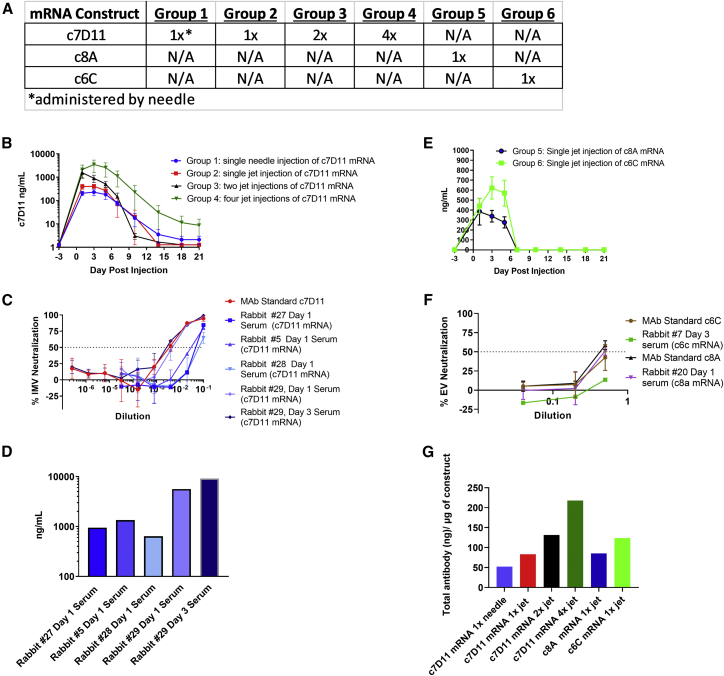
Figure 2.
Intramuscular administration of mRNA constructs in rabbits
(A) Design outline: mRNA encoding c7D11, c8A, or c6C was injected once (groups 1, 2, 5, 6, and 7), twice (group 3), or four times (group 4) by either needle (group 1) or jet injection (groups 2, 3, 4, and 7). (B and E) Temporally collected sera from rabbits were diluted and analyzed by a quantitative, immunogen-specific ELISA using poxvirus antigen, L1 (B) or c6C (E) or c8A (E). (C and F) Serial dilutions of sera from select rabbits and time points were tested for the ability to neutralize the intracellular (MV) form (C) or the extracellular (EV) form (F) of VacV-IHDJ using plaque reduction neutralization test/assay (PRNT). Purified monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) c7D11 (at 10 μg/mL), c6C (at 1 μg/mL), and c8A (at 1 μg/mL) were utilized as controls. (D) L1-immunogen-specific ELISA mean titers corresponding to samples utilized for neutralization testing in (C). (G) Mean peak concentrations as determined by ELISA were normalized by calculating the total theoretical antibody per rabbit (average peak concentration per group multiplied by the average weight of rabbits multiplied by the average blood volume per kilogram [56 mL/kg]) and dividing by the amount of construct (micrograms) administered. Mean and standard error of the mean are given for (B) and (E). Mean and standard deviation are given for (C) and (F).