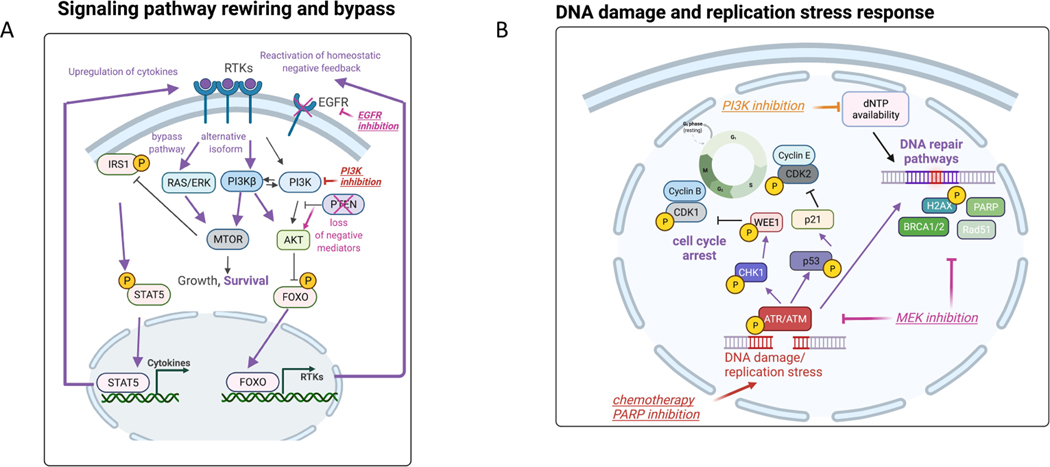
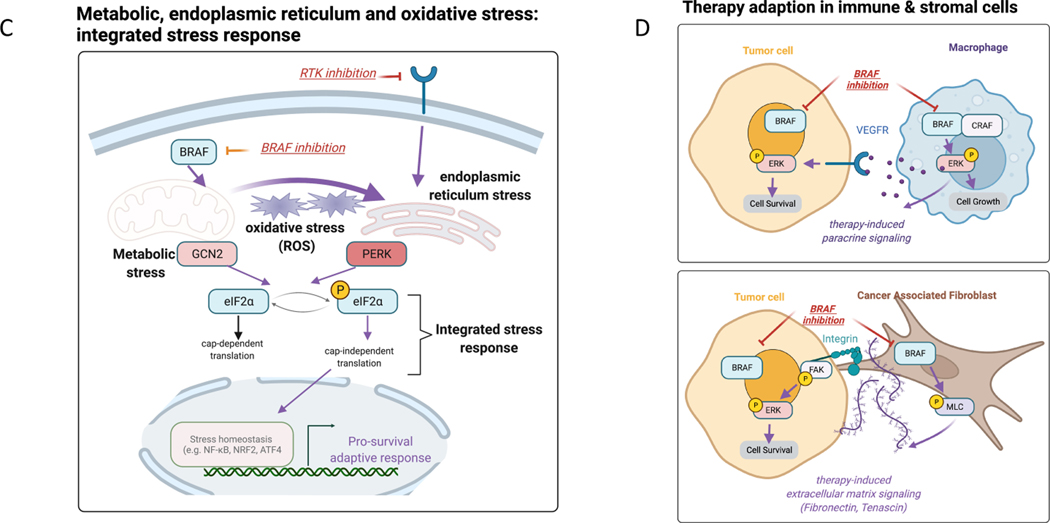
Figure 2: Adaptive response programs in tumor cells and in the tumor ecosystem.
(A) Examples of adaptive responses that bypass inhibition of the PI3K/mTOR pathway: 1) Transcriptional upregulation of RTKs via FOXO transcription factors, 2) secretion of autocrine growth factors via release of the mTOR-driven IRS1 negative feedback loop and 3) utilization of a non-targeted isoform of PI3K. We also highlight another example of signaling rewiring following EGFR inhibition due to downregulation of negative mediators in the PI3K pathway such as PTEN. Purple bolded arrows indicate adaptive responses following each targeted therapy (e.g. EGFRi, PI3Ki, PARPi, MEKi). (B) Engagement of DNA repair pathways to mitigate DNA damage and replication stress. DNA damaging anti-cancer therapies (examples of chemotherapy and PARP inhibition) induce activation of DNA integrity sensors ATM/ATR that induce cell cycle arrest and active DNA repair pathways. PI3K inhibition promotes DNA damage by depletion of nucleoside availability that is required for DNA repair. MEK inhibition represents another example that decreases the levels of DNA repair pathway members resulting in elevated DNA damage. (C) Stress response pathways feed into kinases that phosphorylate eIF2α to induce cap-independent translation of transcription factors that regulate stress homeostasis (integrated stress response). For example, BRAF inhibition mediates metabolic stress via upregulating the upstream kinase GCN2, while RTK inhibition results in PERK upregulation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Targeted therapies (e.g. BRAFi) can also result in unbalanced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that via the same eIF2α kinases engage ROS-mitigation programs that are regulated by transcription factors such as NRF2 and NFkB. (D) Tumor-immune paracrine signaling following BRAF inhibition that mediates immunoevasion (proliferation of pro-tumor M2 macrophages) and reactivation of ERK in tumor cells via macrophage-derived VEGF. BRAF inhibition has also been shown to reactivate focal adhesion kinase-driven ERK in melanoma cells via cancer associated fibroblast-mediated extracellular matrix remodeling. Purple bolded arrows indicate adaptive responses resulting from cell-cell communication.