Figure 1. Crh mRNA levels in the anterior CeA increase upon chronic intermittent alcohol exposure.
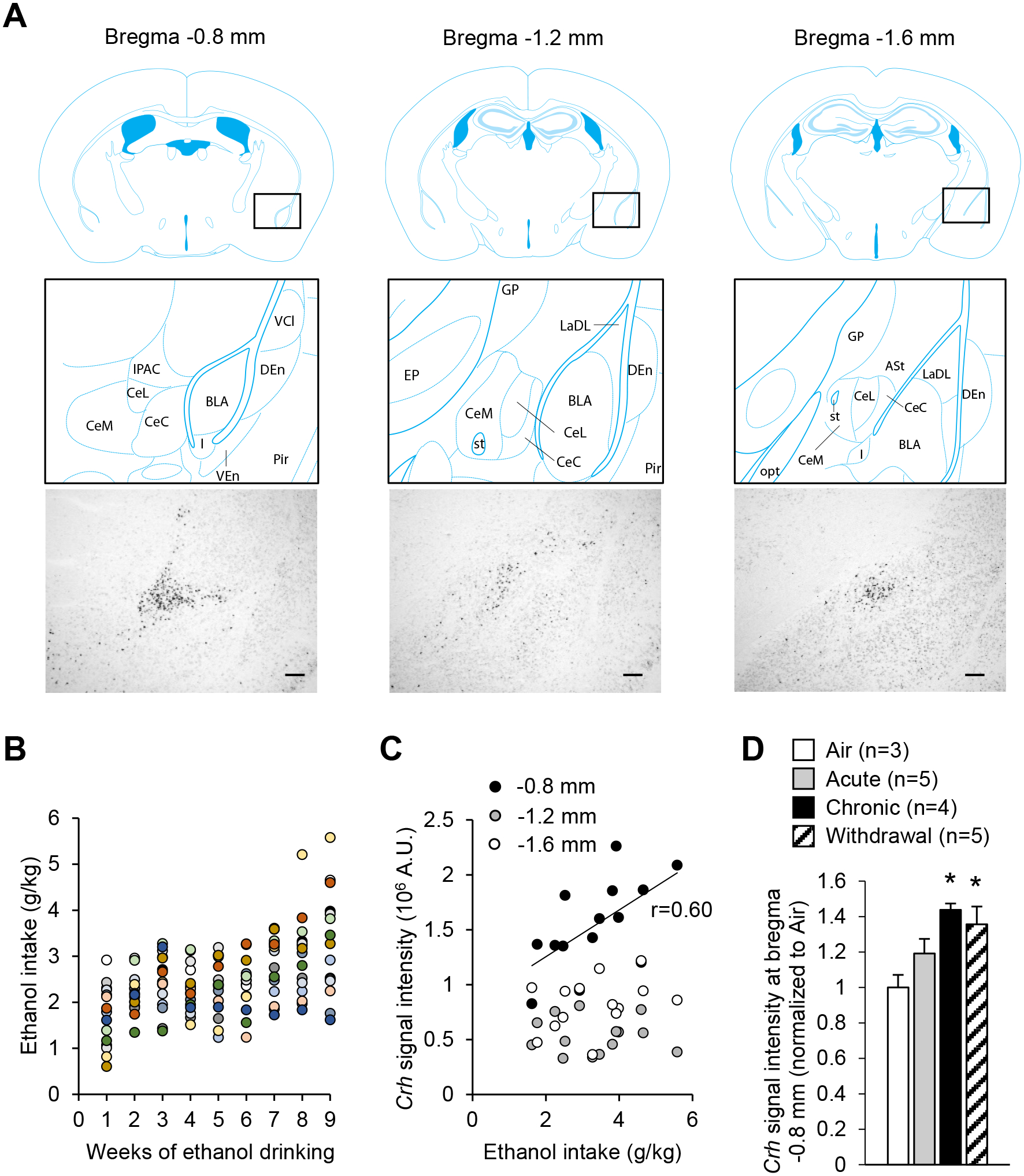
A. Representative images of Crh mRNA distribution at three antero-posterior levels of the mouse CeA (scale bars = 200 μm) and corresponding brain atlas diagrams highlighting a V-shaped cluster of CRF neurons at the junction of the anterior CeL and IPAC (left panels), and scattered CRF neurons at more posterior levels of the CeL (middle and right panels). Brain atlas diagrams were reproduced from85. BLA, basolateral amygdaloid nucleus; CeC, capsular part of the CeA; CeL, lateral division of the CeA; CeM, medial division of the CeA; DEn, dorsal endopiriform claustrum; EP, entopeduncular nucleus; IPAC, interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure; GP, globus pallidus; I, intercalated nuclei of the amygdala; LaDL, lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsolateral part; opt, optic tract; Pir, piriform cortex; st, stria terminalis; VCl, ventral part of claustrum; VEn, ventral endopiriform claustrum. B. Average weekly ethanol intake in a cohort of mice subjected to 2-h two-bottle choice (ethanol 15% v:v vs water) sessions five days per week for nine weeks. Each color represents an individual mouse. C. Crh chromogenic in situ hybridization signal density at three antero-posterior levels of the CeA as a function of ethanol intake during the last week. There was a significant correlation at the most anterior level (≈ bregma −0.8 mm, p<0.05), but not at more posterior levels. D. Crh chromogenic in situ hybridization signal density at the most anterior level of the CeA in mice exposed to a single 16-h bout of alcohol vapor inhalation (Acute), eight bouts (Chronic), or eight bouts followed by three days of withdrawal (Withdrawal). Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. of Crh signal normalized to Air controls. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA; *, p<0.05 vs. Air, Dunnett’s posthoc test.
