Figure 4. CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors exert differential effects in distinct immune cell populations.
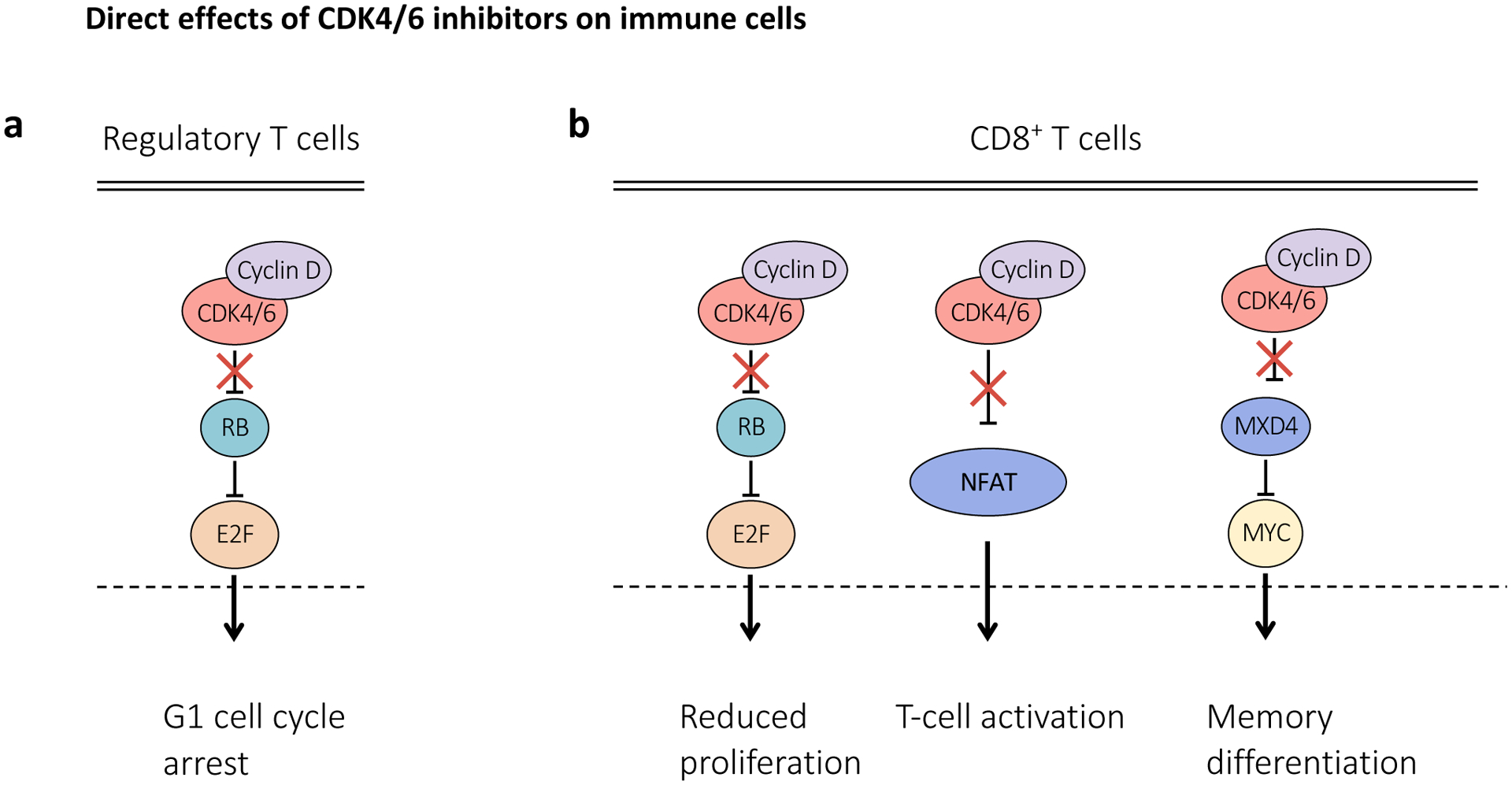
a, Upon treatment with cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK4) and CDK6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors, regulatory T (Treg) cells preferentially undergo cell cycle arrest, likely due to increased reliance on CDK4/6 signalling for cell cycle progression. b, CDK4/6 inhibition enhances CD8+ T-cell activation and induction of effector function via upregulation of nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) signalling. In addition, CDK4/6 inhibitors have been shown to promote memory T-cell differentiation through RB-dependent and RB-independent (increased MXD4 gene expression) mechanisms. MXD4, MAX dimerization protein 4.
