Figure 5. Novel approaches for the use of CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors.
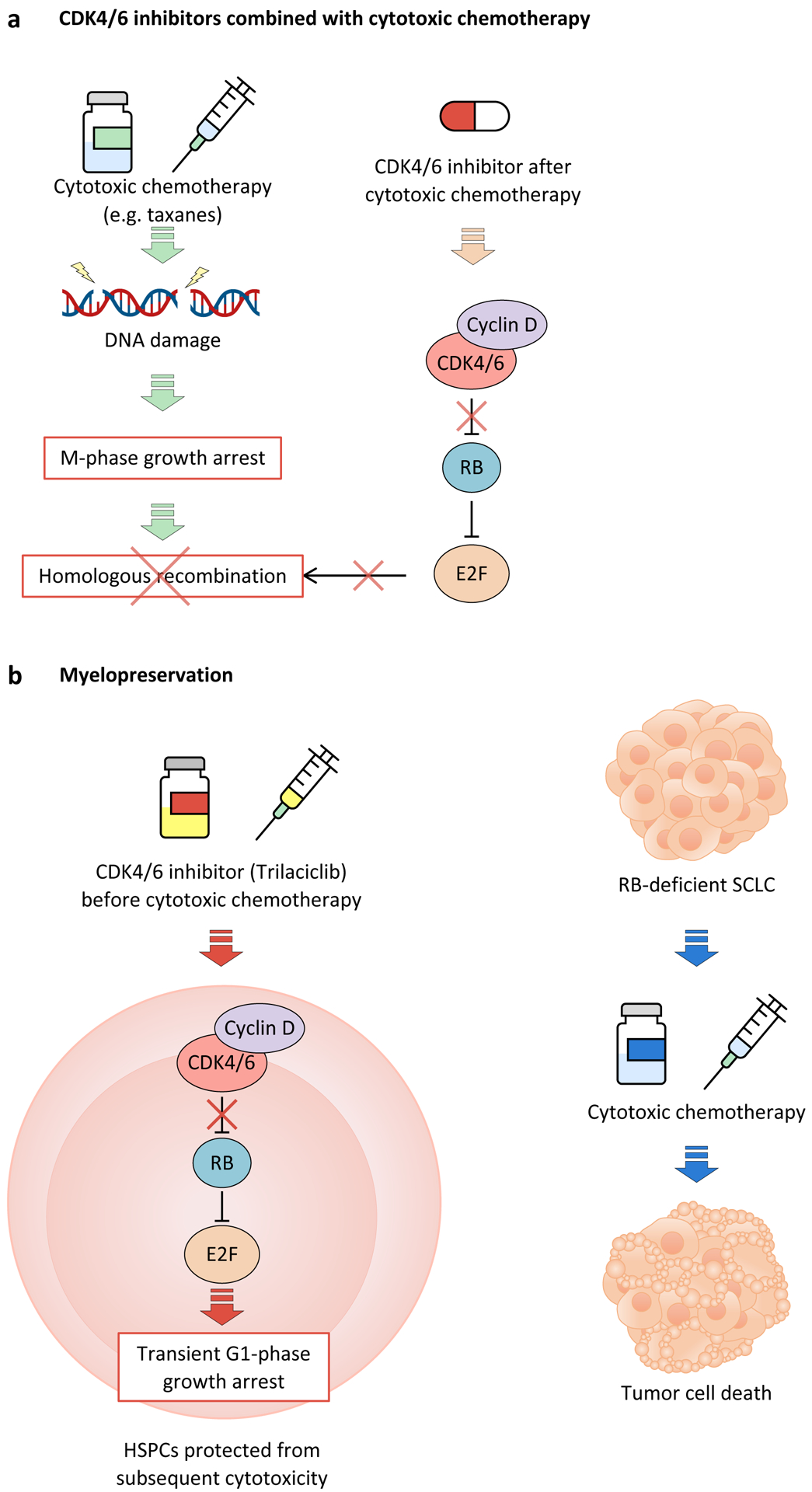
a, Administration of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and CDK6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors after cytotoxic chemotherapy has been shown to enhance response by preventing E2F-mediated DNA damage repair after growth arrest during M-phase. Conversely, treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors prior to chemotherapy would induce G1 cell cycle arrest, thus preventing chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity that occurs during DNA replication or chromosome segregation. b, The CDK4/6 inhibitor trilaciclib can be used to protect hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) from the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy by inducing transient cell cycle arrest prior to treatment with chemotherapy. In this case, the target population would be patients with cancer types that are typically RB-deficient, such as small-cell-lung cancer (SCLC), so as to not interfere with cytotoxicity against tumour cells.
