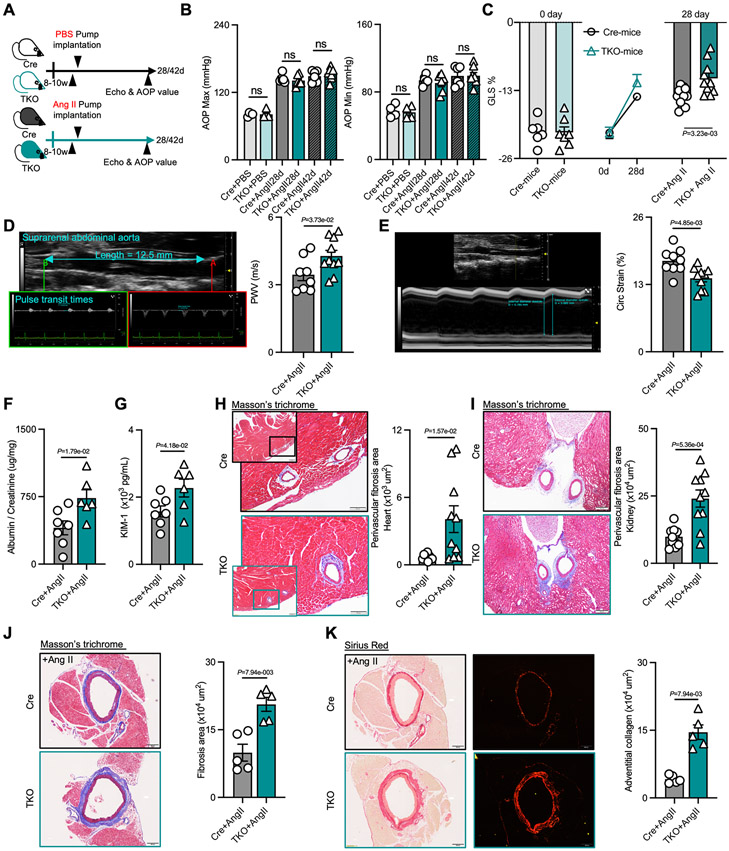
Figure 2. KLF10 deficiency in CD4+ T cells impairs the function of hypertension-related organs and triggers perivascular fibrosis independent of blood pressure.
A, Schematic diagram of experimental set-up of mice groups treated with PBS or Ang II infusion. B, Aortic blood pressure in Cre and TKO mice with PBS (n=4) or Ang II (n=6) treatment for 28 days or 42 days. C, Global longitudinal strain (GLS) in Cre and TKO mice before and after Ang II treatment (n=6 in Cre mice, n=7 in TKO mice, and n=10 in Ang II groups). D-E, Representative ultrasound imaging of the suprarenal abdominal aorta, and measurements of pulse wave velocity (PWV, D) and circumferential strain in Cre (n=8) and TKO mice (n=10) after 28 days of Ang II treatment. F-G, The ratio of albumin and creatinine (F), and the level of kidney injury molecule (KIM)-1 (G) in urine from Cre (n=7) and TKO mice (n=6) after Ang II treatment. H-I, Representative images of Masson trichrome staining, and quantification of perivascular fibrosis in the heart (H, scale bars =100μm) and kidney (I, scale bars= 200μm) (n=10). J-K, Representative images of Masson trichrome staining, and Sirius red staining and quantification of perivascular fibrosis and adventitial collagen in the aorta (n=5, scale bars= 200μm). B-I, P values correspond to unpaired two-tailed t tests. J and K, P values correspond to unpaired two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-tests. Ang II indicates angiotensin II; Echo, echocardiogram; AOP, aortic pressure; ns, not significant; GLS, global longitudinal strain; PWV, pulse wave velocity; Circ Strain, circumferential strain; KIM-1, kidney injury molecule-1.