Fig. 4.
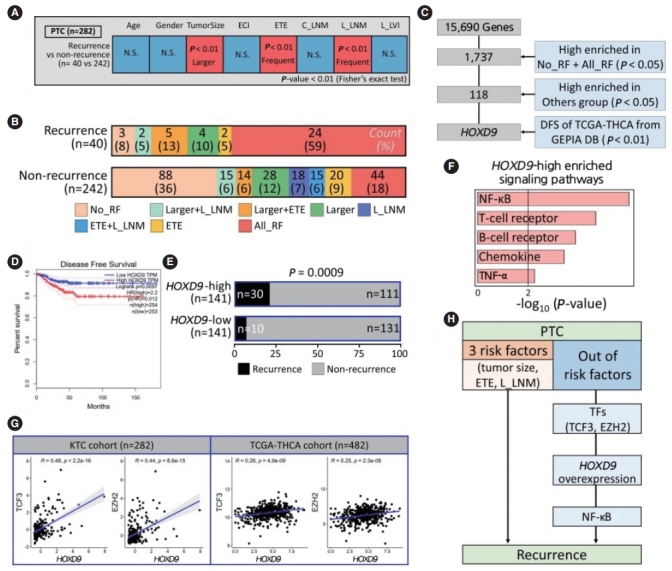
HOXD9 is a candidate gene associated with the recurrence of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). (A) Discovery of recurrence-related factors in PTC samples. The Fisher exact test was performed with a threshold of P<0.01. (B) Barplots showing the spectrum of samples in the PTC group for well-known risk factors such as tumor size, extrathyroidal extension (ETE), and lateral lymph node metastasis (L_LNM). (C) Workflow for selecting HOXD9. (D) Kaplan-Meier plot of thyroid cancer patients based on the expression of HODX9 (high or low based on the median value from the GEPIA database. (E) Barplots showing the recurrence rate based on the expression of HOXD9. (F) Enriched signaling pathways in the HOXD9-high group. (G) Correlation of gene expression between HOXD9 and transcription factors such as transcription factor 3 (TCF3) and enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit (EZH2) that regulate HOXD9 in the Korean Thyroid Cancer (KTC) cohort and the Thyroid Carcinoma cohort from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA-THCA cohort). (H) Summary of the two routes to recurrence from Korean PTC samples. ECI, extracapsular invasion; C_LNM, central lymph node metastasis; L_LVI, lateral-lymphovascular invasion; NS, not significant; RF, risk factor; DFS, disease free survival; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factoralpha; TF, transcription factor.
