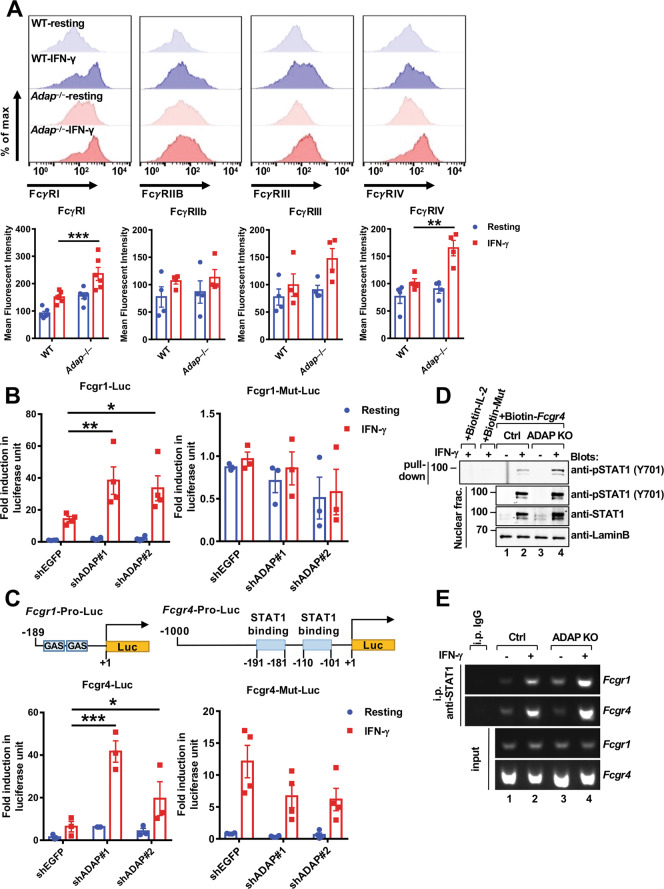
Fig. 3.
ADAP deficiency selectively promotes the transcription and expression of STAT1-targeted genes Fcgr1 and Fcgr4. A FcγR expression on resting and IFN-γ-treated splenic macrophages. Representative histogram by FACS analysis of FcγRI, FcγRIIB, FcγRIII, and FcγRIV on splenic macrophages from WT and Adap−/− mice (n = 4 mice each). Splenocytes were either left unstimulated or stimulated with 10 ng/ml IFN-γ for 18 h. F4/80-positive macrophages were gated out and assessed for FcγR expression. Mean fluorescence intensity was plotted (two-way ANOVA, Sidak’s multiple comparison). B, C Luciferase activity of RAW 264.7 cells transfected with shADAP or shEGFP, together with Fcgr1-Luc or STAT1-binding site mutant-containing Fcgr1-Mut-Luc (B, n ≥ 3, two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison), or Fcgr4-Luc or STAT1-binding site mutant-containing Fcgr4-Mut-Luc reporters (C, n ≥ 3, two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison), followed by stimulation with IFN-γ for 6 h. Schematic diagrams of the reporter constructs are shown in the intermediate panels. D Immunoblot analysis of the biotinylated Fcgr4 promoter probe pull-down precipitates from WT and Adap−/− iBMM cells. Cells were either left unstimulated or stimulated with IFN-γ for 1 h. Nuclear fractions were extracted and incubated with either biotinylated IL-2 promoter as a control, STAT1-binding site mutant-containing Fcgr4 promoter probes (Biotin-Mut) or WT Fcgr4 promoter probes. The biotinylated DNA-protein complexes were pulled down using streptavidin-conjugated agarose beads and subjected to immunoblotting analysis. E ChIP-PCR analysis of the interactions between STAT1 and the Fcgr1 and Fcgr4 promoters in WT and Adap−/− iBMM cells. The Fcgr1 and Fcgr4 promoters were amplified with PCR from the precipitated DNA by anti-STAT1 antibodies. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001