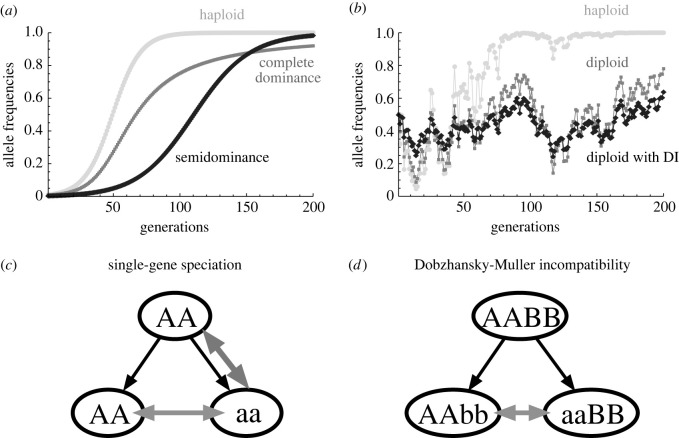
Figure 3.
Examples of the effects of genetic architectures on evolutionary dynamics. (a) The effects of ploidy and allele dominance on evolutionary dynamics under directional selection. Haploid (light grey), diploid with complete dominance (grey) and diploid with semidominance (black) are shown. (b) The effects of ploidy and delayed inheritance (DI) on evolutionary dynamics under temporally fluctuating selection [78]. Haploid (light grey), diploid with complete dominance (grey) and diploid with DI (black) are shown. (c,d) The effects of the number of loci on speciation processes. (c) Single-gene speciation from an ancestral population with an allele A to two populations with alleles A and a where there is reproductive incompatibility between alleles A and a (shown by grey arrows). Because of the incompatibility, it is difficult for a mutant allele a to increase in an ancestral population with a resident allele A. (d) Speciation from an ancestral population with alleles A and B to two populations with alleles A, B, a and b where there is Dobzhansky–Muller incompatibility between alleles a and b due to epistasis. Mutant alleles a and b can increase in an ancestral population without incompatibility unlike the model of single-gene speciation.