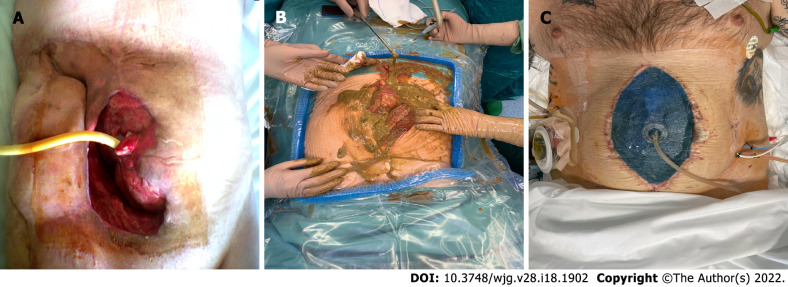
Figure 1.
Intra-abdominal sepsis. A: Abscess in the right iliac fossa, spontaneously draining to the skin, associated with high-flow enteric fistula. Foley catheter placed in the fistulized small intestine; B: Fecal contamination of the peritoneal cavity in a patient with Crohn’s disease with perforation of the transverse colon; C: Open abdomen after treatment of intestinal perforation in Crohn’s disease. Negative pressure intraperitoneal device placement.