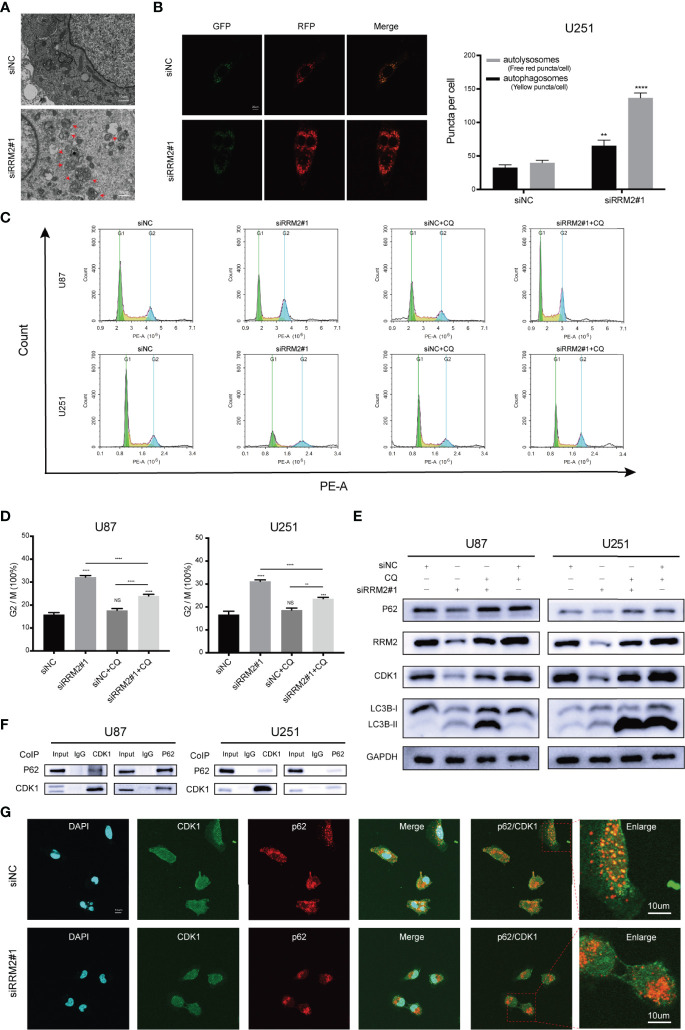
Figure 4.
RRM2 knockdown induces cell cycle arrest in GBM via promoting CDK1 protein degradation by increasing autophagic flux in vitro. (A) TEM images of U251 cells transfected with RRM2 siRNA for 48h. Autophagic vacuole (red arrows). Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) U251 cells transfected with RRM2 siRNA for 48h, autophagic flux was analyzed using the RFP-GFP-LC3 construct. Scale bar: 20 μm. (C, D) After U87 and U251 cells transfected with RRM2 siRNA for 48 h or cultured with CQ (2 μM, 2 h), cells cycle distribution were analyzed using flow cytometry. (green: G0-G1, yellow: S, and blue: G2-M). (E) After U87 and U251 cells transfected with RRM2 siRNA for 48 h or cultured with CQ (2 μM, 2 h), CDK1, RRM2, p62 and LC3B proteins expression were analyzed by western blot assay. (F) Total protein lysates of U87 or U251 cells were prepared for Co-IP using CDK1 or p62 antibody. (G) Immunofluorescence assay of the co-localization of p62 (red) and CDK1 (green) in U251 cells after transfection with RRM2 siRNA for 48 h. Scale bar: 10 μm. The data are presented as the mean ± SD (n=3). NS, non-significant. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.