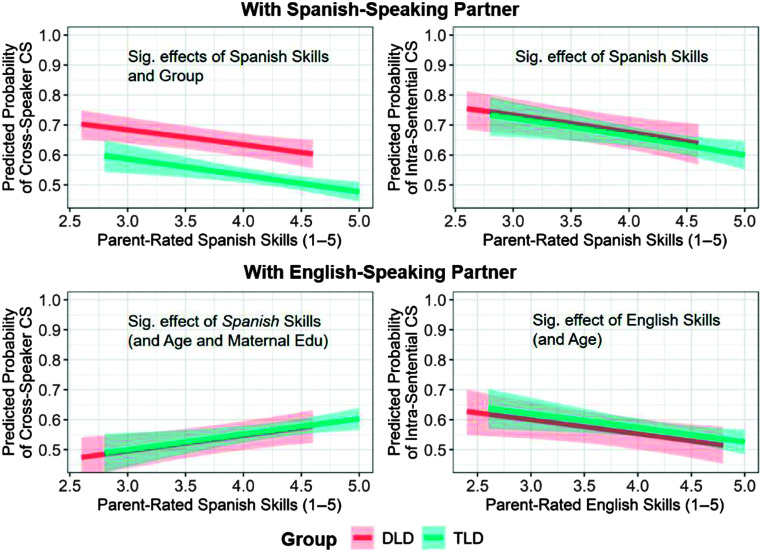
Figure 4.
Model plots showing the effects of group (DLD vs. TLD, shown as the vertical distance between red and blue lines) and Spanish proficiency (shown by the slope of the lines) on the tendency to engage in cross-speaker and intrasentential code-switching with a Spanish-speaking partner (top) and the effects of group and Spanish or English proficiency on the tendency to engage in code-switching with an English-speaking partner (bottom). Proficiency was indexed by average parental ratings on a 1–5 scale across five areas of language (vocabulary, speech production, sentence length, grammaticality, and comprehension) on the Inventory to Assess Language Knowledge (ITALK). Models also included age, maternal education, and proficiency in the other language, which were fixed at their means when generating predicted values for the model plots. Plots were generated using the ggplot2 package Version 3.3.2 (Wickham, 2009). DLD = developmental language disorder; TLD = typical language development.