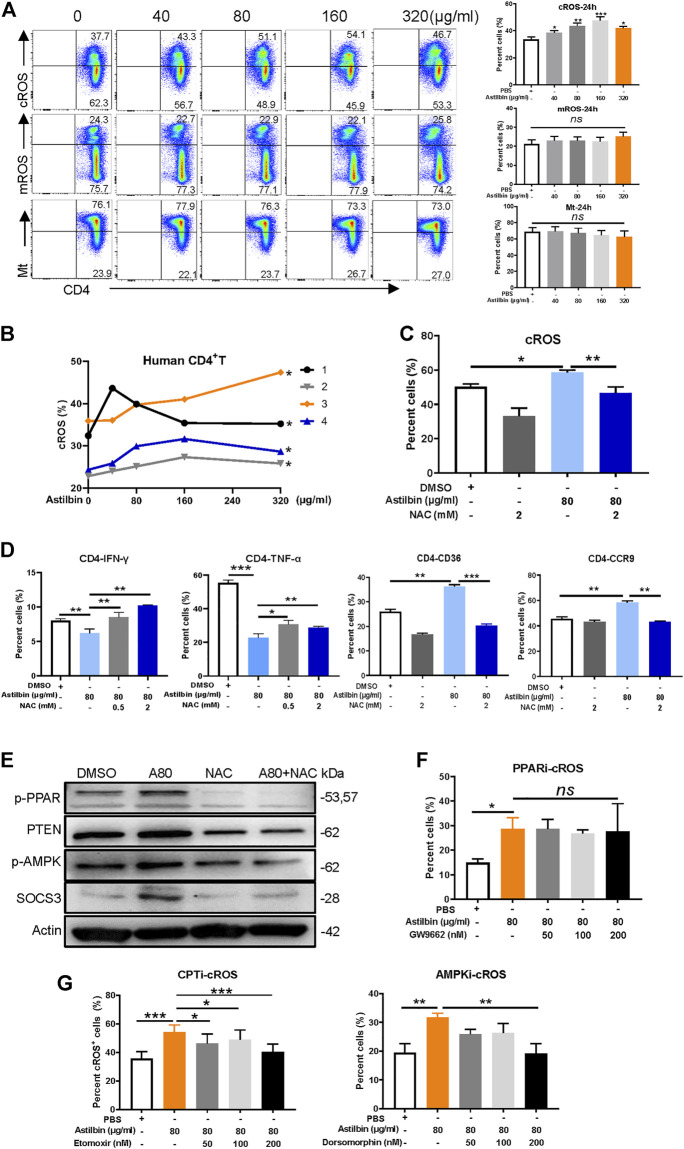
FIGURE 6.
cROS production induced by astilbin in CD4+ T cells. (A) Variations of cytoplasmic ROS, mROS, and mitochondrial weight in murine CD4+ T cells treated with astilbin for 24 h. Mean ± SD; n = 3. (B) Variations of cROS in human CD4+ T cells treated with astilbin. Mean ± SEM; n = 4. (C) Depletion of ROS by NAC (2 mM). Mean ± SD; n = 3. (D) Effects of ROS depletion on IFN-γ, TNF-α, CD36, and CCR9 of astilbin-treated CD4+ T cells. Mean ± SD; n = 3. (E) Effects of ROS depletion on p-PPARγ, PTEN, p-AMPK, and SOCS3 of astilbin-treated CD4+ T cells. Effects of PPARγ inhibition (F) and CPT or AMPK inhibition (G) on cellular ROS production of astilbin-treated CD4+ T cells. Mean ± SD; n = 3. All experiments were conducted at least three times. p values (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ns, no significant difference) determined by one-way ANOVA (A,C,D,F,G) and two-way ANOVA (B).