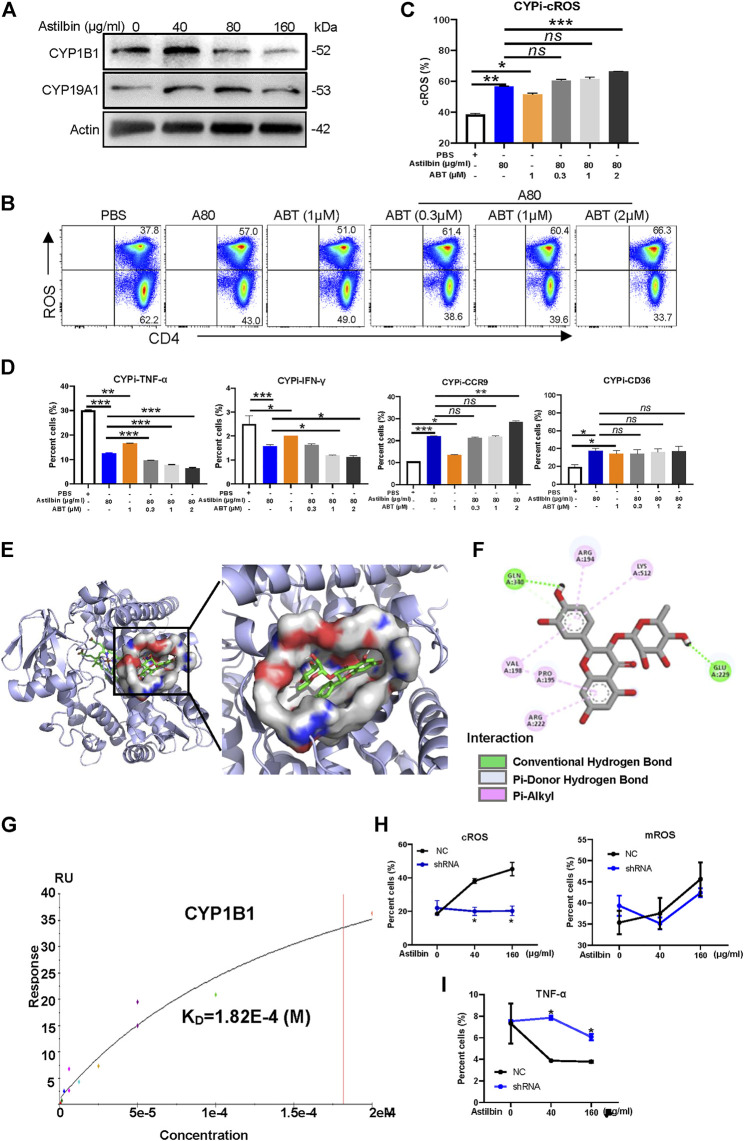
FIGURE 7.
CYP1B1 provides a dock site for astilbin. (A) Variations of CYP1B1 and CYP19A1 in astilbin-treated CD4+ T cells. (B,C) Astilbin promotes cellular ROS production similar to ABT (a non-specific inhibitor of CYP). Mean ± SD; n = 3. (D) Effects of astilbin on IFN-γ, TNF-α, CD36, and CCR9 of CD4+ T cells similar to ABT. Mean ± SD; n = 3. (E) Three-dimensional model of the CYP1B1 active site with bound astilbin. (F) Binding of CYP1B1 with astilbin and the inset showing the principal interactive residues of astilbin at the CYP1B1 binding pocket. Green dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds. The hydrophobic interaction is depicted by pink dashed lines. (G) Real binding of CYP1B1 with astilbin confirmed by SPR assay. Production of cROS and mROS (H) and TNF-α (I) in CYP1B1 shRNA-transfected CD4+ T cells. Mean ± SEM; n = 3. All experiments were performed three times. The inhibitor of CYP, ABT, is abbreviated as CYPi. p values (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ns, no significant difference) determined by one-way ANOVA (C,D) and two-way ANOVA (H,I).