Fig. 7.
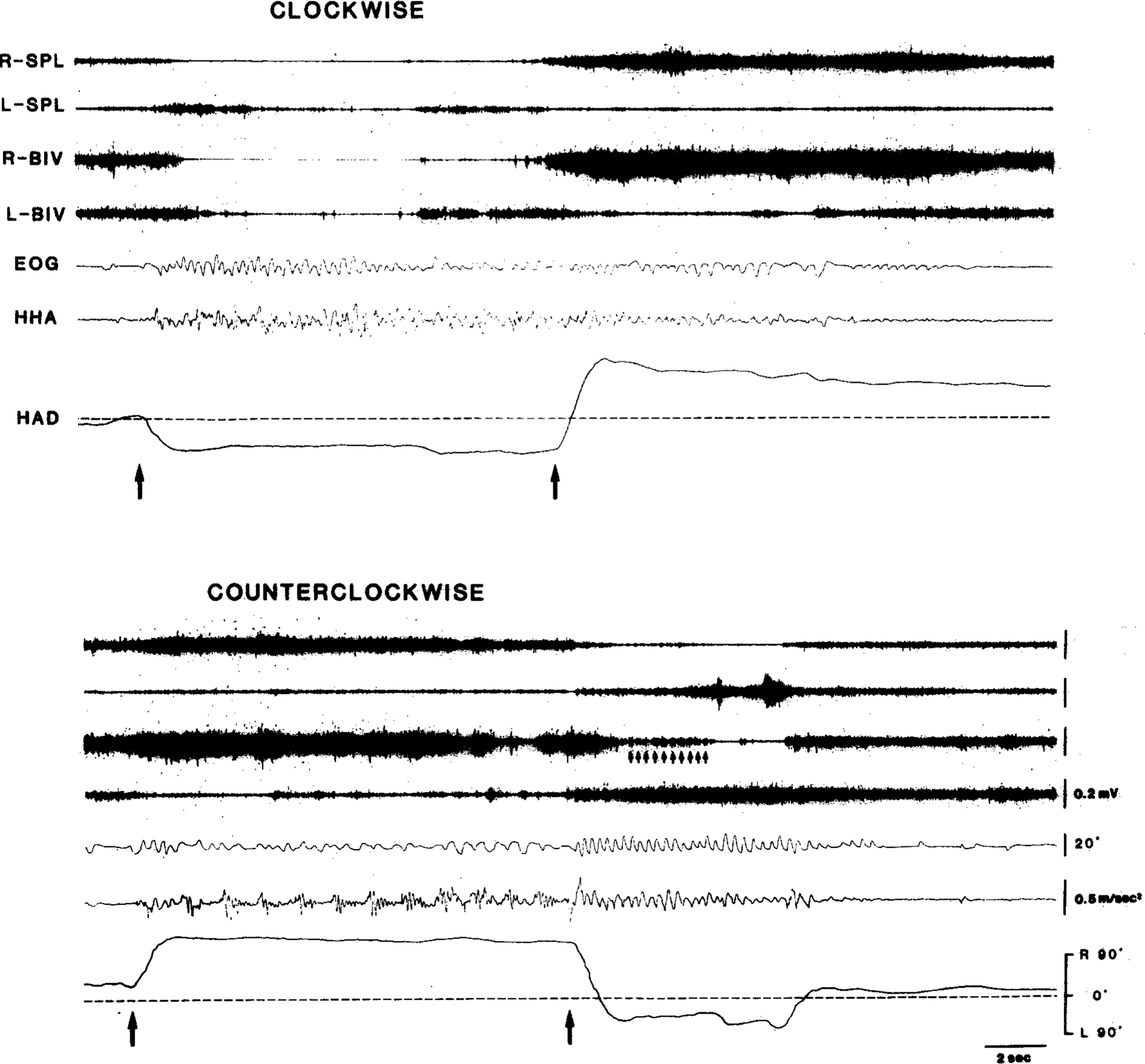
Polygraphic records of horizontal per/postrotatory eye (AC EOG) and head movement after unilateral lesions of the left pontine reticular formation (cat IB-2). Cat on turntable was rotated during period indicated by the two arrows. Note that quick-phase anticompensatory movements of eyes and head toward ipsilateral side (left) during counterclockwise rotation are much weaker than those toward contralateral side during clockwise rotation and after counterclockwise rotation. Also, note that HAD representing compensatory head posture is abnormally large toward contralateral side during counterclockwise rotation and after clockwise rotation. Small arrows in bottom panel indicate EMG bursts corresponding to postrotatory nystagmic, quick-phase eye-movements toward intact side. Upward deflections in both EOG and HHA traced indicate movements to right. HHA, horizontal head angular acceleration; HAD, horizontal head angular deviation.
