FIGURE 4.
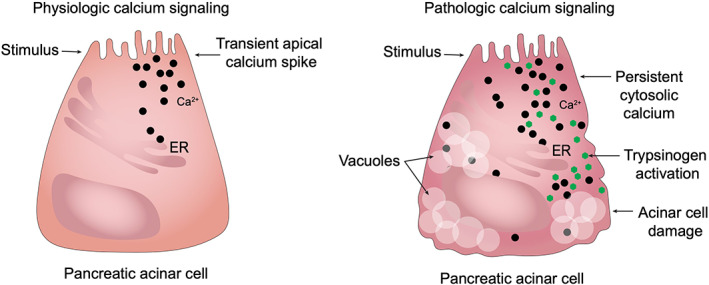
Persistent cytosolic calcium accumulation in AP. Under physiologic conditions there is a transient spike in apical calcium concentration, which results in release of digestive zymogens from the apical border of the pancreatic acinar cell. During AP there is a global and persistent increase in cytosolic calcium concentration, which causes calcium overload, premature trypsinogen activation and subsequent acinar cell damage. Deranged calcium signaling is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction
