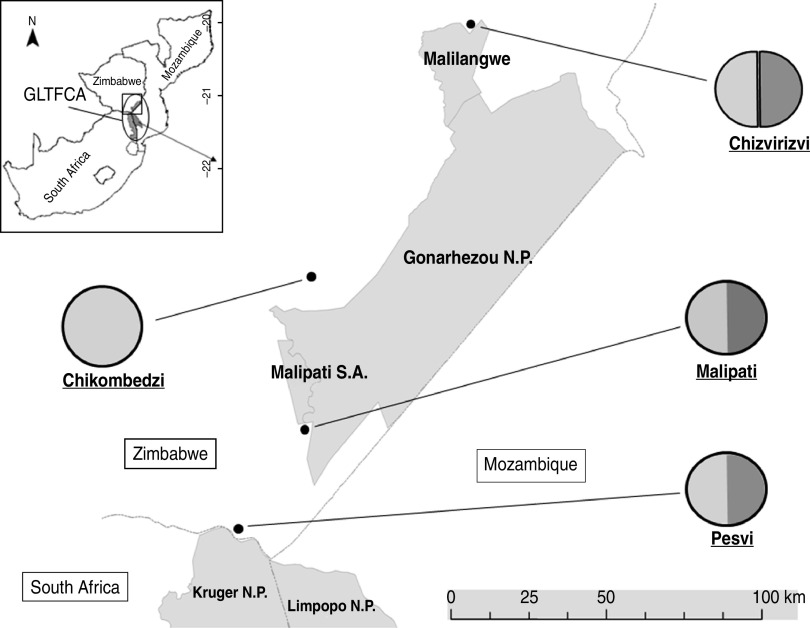
Fig. 1.
Study sites and different wildlife/livestock interfaces. The map (top left) presents the south-eastern part of southern Africa encompassing Mozambique, South Africa and Zimbabwe. The Great Limpopo Transfrontier Conservation Area (GLTFCA) is represented by an ellipse and a square indicates the zoom for the rest of the Figure. On the main map, the grey area represents protected areas, N.P. indicates National Parks, Malilangwe is a conservancy and Malipati S.A. refers to the Malipati Safari Area, a hunting concession. The single line represents international borders. Each village representing a sampling unit in the study is indicated by a black dot and the circle linked to this dot refers to the type of wildlife/livestock interface: light grey represents livestock and dark grey represents wildlife; the double vertical line separating the circle indicates a fenced interface and a difference in level of shading represents an interface with no fence.