Figure 1. Dietary interventions for sensitizing to ICIs targeting PD-1/PD-L1.
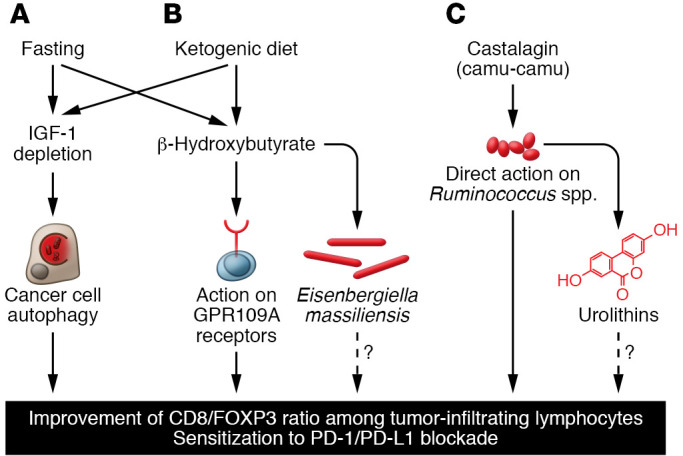
(A) Mechanisms of fasting-induced immunostimulation. Fasting causes a reduction of circulating IGF1 levels, which stimulates autophagy in cancer cells. (B) Ketogenic diet and its effects on the patient. Increased levels of the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate stimulate GPR109A receptors expressed by immune cells and modify the gut microbiota (C) Supplementation with camu-camu–derived castalagin. In the intestinal lumen, castalagin directly acts on specific Ruminococcus species to stimulate their expansion. Some bacterial species, including Ruminococcus species, metabolize castalagin into urolithins, which might have immunostimulatory effects as well. All three dietary interventions modify the tumor microenvironment, hence enhancing the CD8/FOXP3 ratio in the immune infiltrate and sensitizing to immune checkpoint inhibition targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction.
