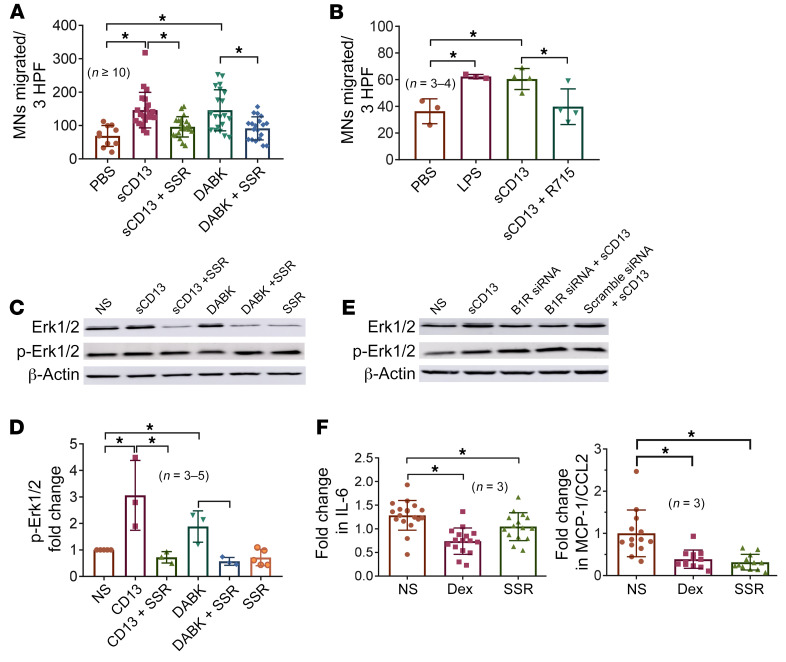
Figure 4. B1R antagonist inhibits sCD13-mediated MN migration, FLS signaling, and cytokine production.
(A) SSR240612 (n = 21) significantly inhibited sCD13-induced MN migration (n = 21). DABK-induced MN migration (n = 20) was also inhibited by SSR240612 (n = 20), suggesting that DABK and sCD13 are 2 ligands of B1R. PBS (n = 10) was used as a negative control. n = number of wells. HPF, high-power fields. (B) Another B1R inhibitor, R715 (n = 4), also significantly inhibited sCD13-induced MN migration (n = 4). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS, n = 3) and PBS (n = 3) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. n = number of assays. (C) sCD13- or DABK-stimulated phospho-Erk1/2 was significantly reduced by SSR240612 in RA FLSs from 4 different patients. (D) Quantification of Western blots. n = number of blots. (E) RA FLSs transfected with a B1R-silencing construct showed that sCD13-stimulated Erk1/2 phosphorylation was markedly decreased in comparison with scrambled RNA. (F) B1R inhibitor SSR240612 inhibited cytokines MCP-1/CCL2 and IL-6 in RA ST. Dexamethasone was used as a control for cytokine inhibition. n = number of replicates from 3 RA patients. Results represent the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05. Significance was determined by Kruskal-Wallis test (A) and 1-way ANOVA (B, D, and F). SSR, SSR240612; NS, nonstimulated; Dex, dexamethasone.