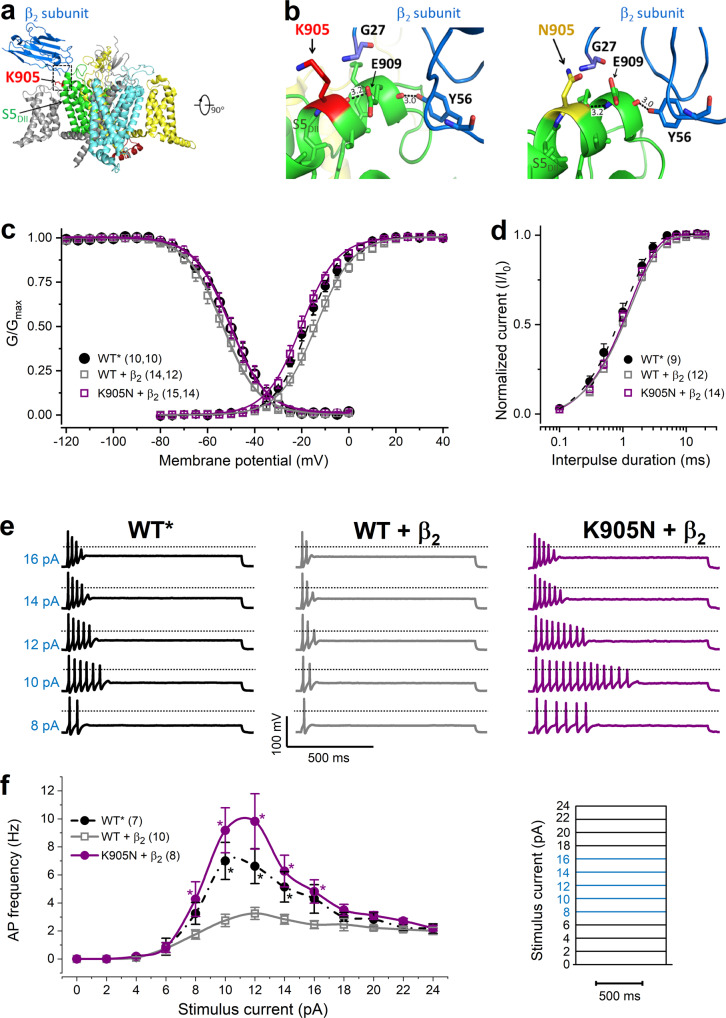
Fig. 5. Gain-of-function characteristics of the K905N variant are revealed in the presence of β2 subunit.
a 3D structure of the wild-type Nav1.2 channel-β2 subunit complex (PDB accession no. 6J8E24) showing the four main channel domains DI–IV (DI, gray; DII green; DIII, yellow; DIV, cyan) and the β2 subunit (blue). b Structure-predicted interactions between the α1-subunit S5DII region and the β2-subunit. Expanded views of the helix in segment 5 of domain II (S5DII) (boxed area in A) showing the positively charged K905 (wild-type, left) and the polar, uncharged side chain residue N905 (mutant, right). All residues within 5 Å distance from K905 or N905 are shown in stick representation (blue: nitrogen, red: oxygen). c Activation and inactivation curves, obtained by non-linear least-squares fits of Boltzmann equations (Eq. (1)) to data points (WT alone, black solid circle; WT + β2, gray open square; K905N + β2, purple solid circle); see the parameters of the fits in the Supplementary Table 9; n values, the number of independent experiments for inactivation and activation (first and second number, respectively), are shown in parentheses. d Recovery from fast inactivation. The time constants of recovery (τ), included in Supplementary Table 9, were obtained by fitting a single exponential function to the data (Eq. (3)) (symbol definition same as in c). Statistical evaluation of data in c and d (one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test) is shown in Supplementary Table 9. e Representative examples of action potential firing in response to depolarizing step current stimuli (8–16, 2 pA steps, 1 s duration) in DAPC experiments using gNav1.6 = 0 and gKv = 2 settings; the corresponding step stimuli are highlighted in blue in the stimulus protocol shown in (f); the dotted lines indicate 0 mV. f Input–output relationships showing the dependence of the action potential firing on stimulus current magnitude. Firing of the hybrid AIS neuron incorporating WT (black solid circle), WT + β2 (gray open square), or K905N + β2 (purple solid circle) was elicited by current steps in the range between 0 and 24 pA, in 2 pA increments (inset protocol). Data in c−f are mean ± SEM; n values, the number of independent experiments, are shown in parentheses. Differences in firing activity elicited at various current amplitudes were evaluated with two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test; asterisks indicate P < 0.05 (for individual P values see Supplementary Table 10). Action potential characteristics are summarized in Supplementary Table 11.