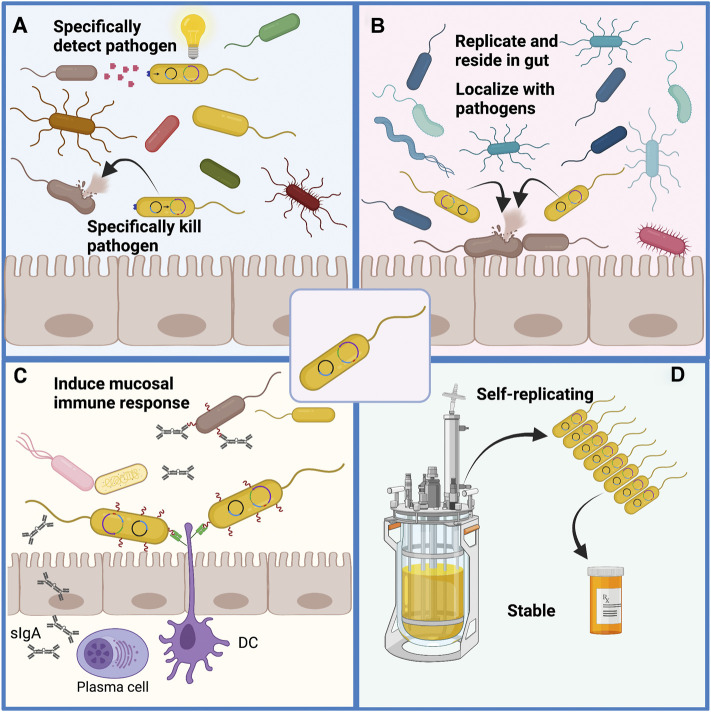
FIGURE 4.
Potential benefits of engineered live cell therapeutics. (A) Engineered probiotics have the potential to be trained to detect specific pathogens by way of signaling molecules, surface antigens, secreted metabolites or other small molecules unique to the pathogen. This high specificity may allow for selective killing of the pathogen without loss of the resident microbial population, thus avoiding the dysbiosis that results from administration of broad-spectrum antibiotic drugs. (B) An engineered probiotic would reside in the gut in close proximity to sites of infection to allow direct and specific killing of intestinal pathogens with limited systemic effects. As the probiotic would self-replicate it would be effective for a prolonged time without the need for multiple applications. (C) As a live-cell vaccine, probiotics can act as a delivery vehicle to secrete or display pathogen surface antigens, adhesion molecules or toxin fragments to induce mucosal immunity at the site of infection which may have benefits over systemic immunization. (D) Engineered live-cell therapeutics can be produced in large quantity relatively cheaply through bioreactor culture and the cells can be stored dry or frozen with high viability.