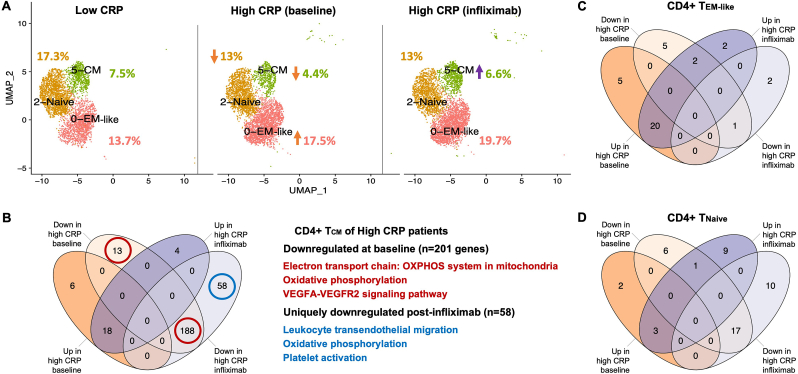
Fig. 3.
Cellular and molecular shifts in CD4+ T cell clusters in MD with high inflammation and response to infliximab. Shifts in the CD4+ T cell compartment included ∼30% and ∼10% lower abundance of CD4+ central memory T cells (TCM) and Tnaive cells respectively as well as ∼50% higher abundance in a cluster consistent with effector memory-like (TEM-like) cells in high CRP patients (N = 3 per group). Orange and purple arrows indicate direction of changes in cell abundance as % of PBMCs in high vs low CRP and high CRP baseline vs post-infliximab comparisons (A). The numbers of differentially expressed genes in TCM cells of high CRP patients at baseline and post-infliximab are shown along with representative pathways enriched by genes downregulated at baseline (red circles) or uniquely downregulated post-infliximab (blue circle)(B). The numbers of differentially expressed in TEM-like (C) and Tnaive cells (D) of high CRP patients at baseline and post-infliximab. CRP, C-reactive protein; UMAP, uniform manifold approximation and projection; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor-1; EM, effector memory; CM, central memory; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor A; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)