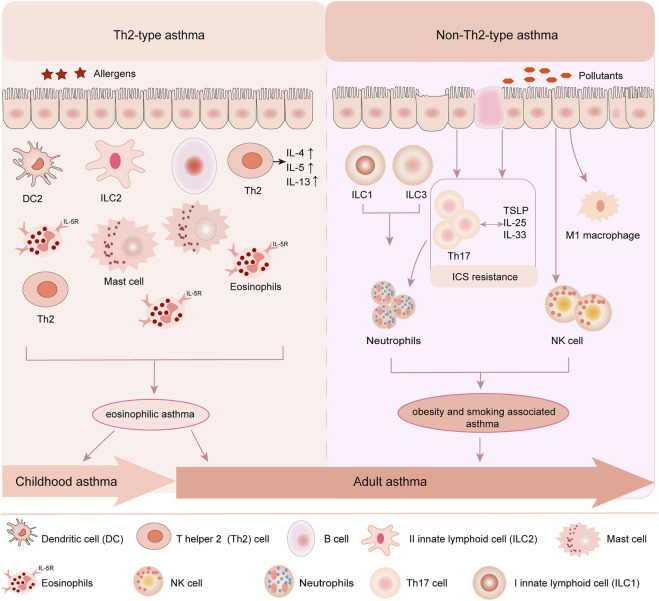
FIGURE 1.
Childhood asthma and adult asthma phenotypes. Childhood asthma and adult asthma are crossed and different in phenotypes. In children, Th2-type asthma is the main common type. Allergen stimulates the recruitment of inflammatory cells such as eosinophils, the proliferation and activation of immune cells such as mast cells and DCs, and induces the injury of airway epithelial cells, which lead to the release of inflammatory factors and Th2 cytokines, such as IL4, IL5 and IL13. In adult, both Th2-type and non-Th2-type asthma are two common types. Upon pollutants stimulation, type I innate lymphoid cells (ILC1) and type III innate lymphoid cells activation (ILC3) activate neutrophils and airway epithelial cells to drive the proliferation of Th17 cells which mediates in turn neutrophil recruitment. Pollutants also contribute to M1 macrophage and NK cell recruitment to the airways, resulting in non-Th2-type asthma in adult.