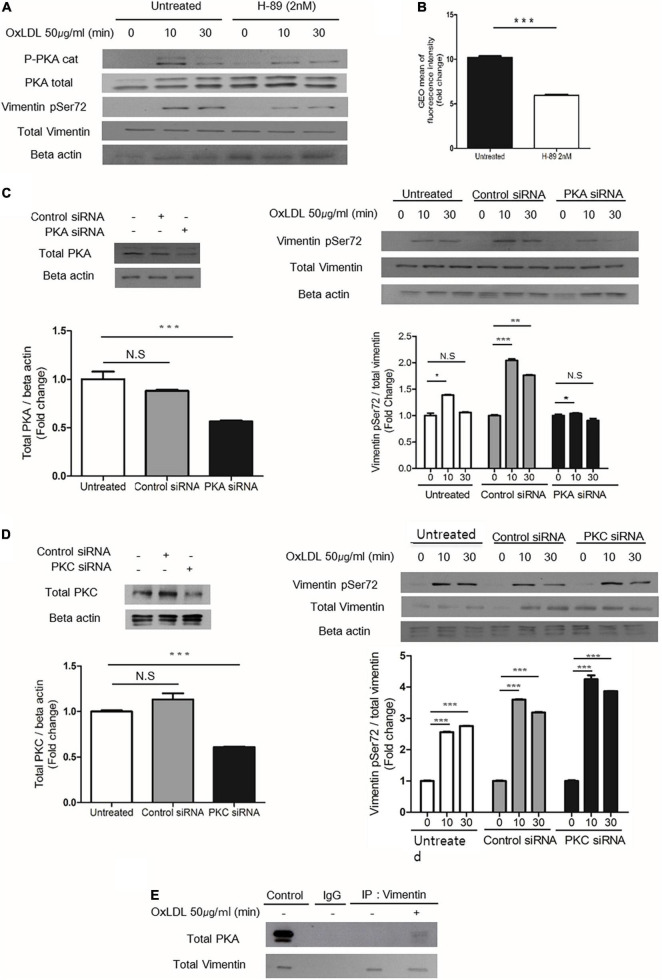
FIGURE 5.
PKA mediates oxLDL-induced vimentin (Ser72) phosphorylation. (A) Wild type murine peritoneal macrophages pretreated with H-89(2 nM), a specific PKA inhibitor were incubated with oxLDL (50 μg/ml) for indicated times. The lysates were analyzed by immunoblot for phosphorylated vimentin (Ser72) and total vimentin. Beta actin was used for internal control. (B) Flow cytometry data. BMDMs were pretreated with or without H-89 (2 nM) and then exposed to DiI- oxLDL (50 μg/ml) for 5 min. The fluorescence intensities of these cells were measured. (C) Left, Western blot analysis for PKA was performed using cell lysates of wild type murine BMDM transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against PKA. Cells were lysed 24 h after the siRNA treatment and analyzed by immunoblot for PKA. Right: Wild type murine BMDMs were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against PKA and incubated with oxLDL (50 μg/ml) for indicated times and analyzed by western blot. (D) Left: Western blot analysis for PKC was performed using cell lysates of wild type murine BMDM transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against PKC. Cells were lysed 24 h after the siRNA treatment and analyzed by immunoblotting to confirm the suppression of PKC expression. Right: Wild type murine BMDMs were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against PKC and incubated with oxLDL (50 μg/ml) for indicated times and analyzed by western blot. (E) Vim +/+ murine peritoneal macrophages were treated with or without oxLDL (50 μg/ml) for 10 min and immunoprecipitated with anti-vimentin antibody. The precipitants were analyzed by western blot for PKA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.