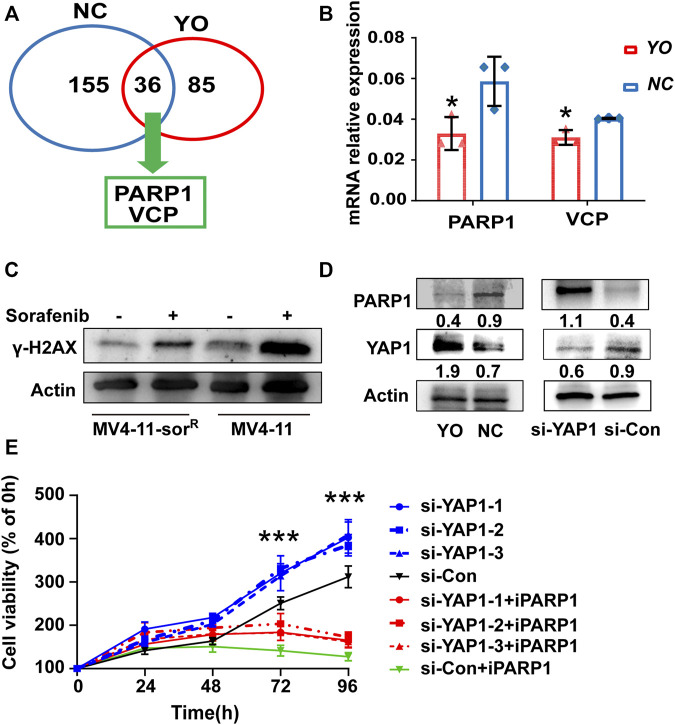
FIGURE 3.
YAP1 suppression promoted FLT3-ITD+ AML cell resistance through DNA damage response dependent of PARP1. (A) Mass spectrometry analyzed selected proteins (Score Sequest HT ≥ 1.5) of YO (red) and NC (blue) cells. (B) RT-qPCR detected the mRNA expression level of PARP1 and VCP in YO and NC cells. (C) γ-H2AX protein expression of MV4-11-sorR and MV4-11 cells was examined after 6 h of treatment with or without sorafenib (50 nM). (D) PARP1 and YAP1 protein expression was analyzed by Western blot in YO and NC cells as well as in YAP1 knockdown (si-YAP1) and non-silencing scrambled control (si-Con) cells, respectively. (E) Proliferation of si-YAP1 and si-Con cells with or without PARP1 inhibitor Olaparib (iPARP1) was assessed by CCK8 assays, and viable cell rates at 12, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h were calculated normalized to the absorbance at 0 h. Data are shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.