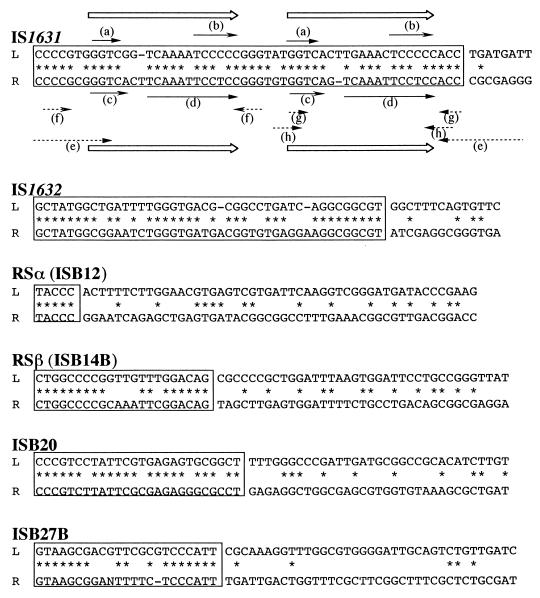
FIG. 2.
Comparison of sequences of putative TIRs of IS elements isolated from B. japonicum HRS strains. “L” denotes sequences at the 5′ (left) end, and “R” denotes complementary sequences at the 3′ (right) end, of the elements. Boxed and asterisked nucleotides are identical in and around the L and R sequences of the putative TIRs. For IS1631, peculiar structural features in and around the TIR are emphasized by solid arrows (short direct repeats) and dashed arrows (inverted repeats). The left TIR (nucleotides 1 to 53) contained 5′-GGTC (a) and 5′-TCCCCC (b) sequences repeated in a direct orientation. The right TIR (nucleotides 2660 to 2712) contained 5′-TGACC (c) and 5′-TCAAATTCCTCC (d) sequences repeated in a direct orientation. Only the right TIR contained four pairs of short inverted repeats that could form various hairpin structures: a 10-bp sequence with a 1-base mismatch (e), two 4-bp sequences (f and h), and a 3-bp sequence (g). IS1631 TIRs seem to be composed of consensus repeats (18 or 19 bp) of 5′-GGTCNN(N)TNAAANTCCNCC-3′ (open arrows), which is a common feature of the IS21 family (13).