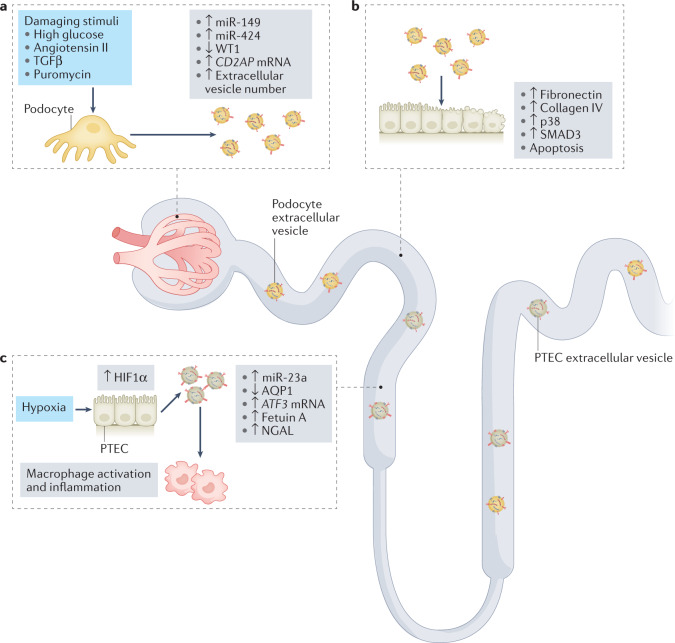
Fig. 2. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the amplification of kidney damage.
Urinary extracellular vesicles can mediate crosstalk between nephron compartments. a | Damaging stimuli induce an increase in the release of podocyte extracellular vesicles29 and modulate their content28. Upregulation of CD2AP mRNA and downregulation of Wilms tumour protein 1 (WT1) in extracellular vesicles are potential biomarkers of podocyte damage. b | Extracellular vesicles released from damaged podocytes can be taken up by proximal tubule epithelial cells (PTECs) and induce apoptosis (potentially via transfer of miR-149 and miR-424)28 and activation of pro-fibrotic pathways, resulting in phosphorylation of p38 and mothers against decapentaplegic homologue 3 (SMAD3) and upregulation of fibronectin and collagen IV30. c | In response to hypoxia, PTECs upregulate hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) and shed extracellular vesicles that express miR-23a. These exosomes promote macrophage activation and inflammation32. Downregulation of aquaporin 1 (AQP1) and upregulation of ATF3 mRNA, fetuin A and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in extracellular vesicles are potential biomarkers of tubular damage. TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β.