Fig. 1.
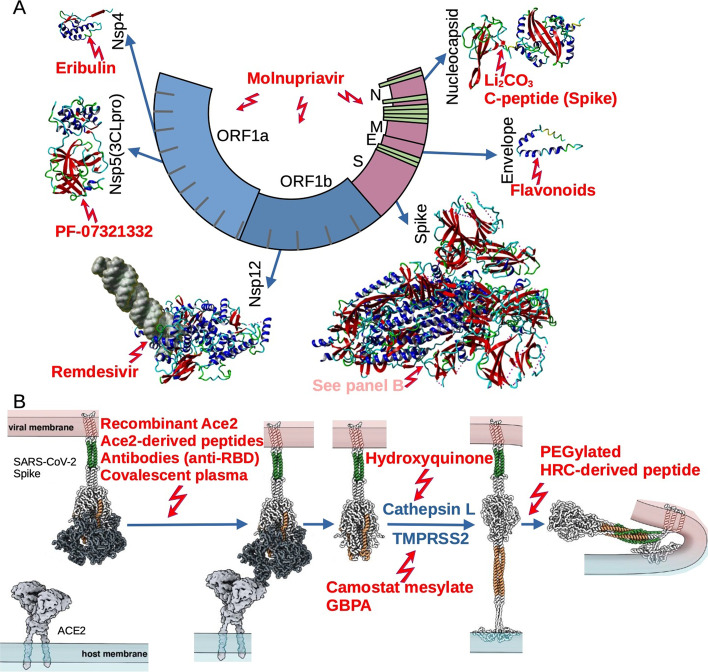
Most promising anti-COVID-19 therapeutics and their molecular targets. A Schematic diagram of SARC-CoV-2 genome comprising 14 ORFs encoding structural and nonstructural (Nsp) proteins, which can be targeted by a range of various compounds; structural models were generated according to atomic coordinates accessible in RCSB PDB database: 3GFZ (C-terminal domain of Nsp4 from feline coronavirus), 6LU7 (SARS-CoV-2 main protease complex, Nsp5), 6YYT (SARS-CoV-2 Nsp12 bound to RNA), 6VYB (SARS-CoV-2 spike ectodomain in open state), 5X29 (envelope protein of SARS-CoV), 6VYO, and 6YUN (N-terminal and C-terminal domain on nucleocapsid phosphoprotein from SARS-CoV-2, respectively). B Proposed model of interactions between spike protein on the viral membrane and ACE2 on the host cell surface leading to membrane fusion. The process can be inhibited via various compounds at different stages
(structural models adapted from [90])