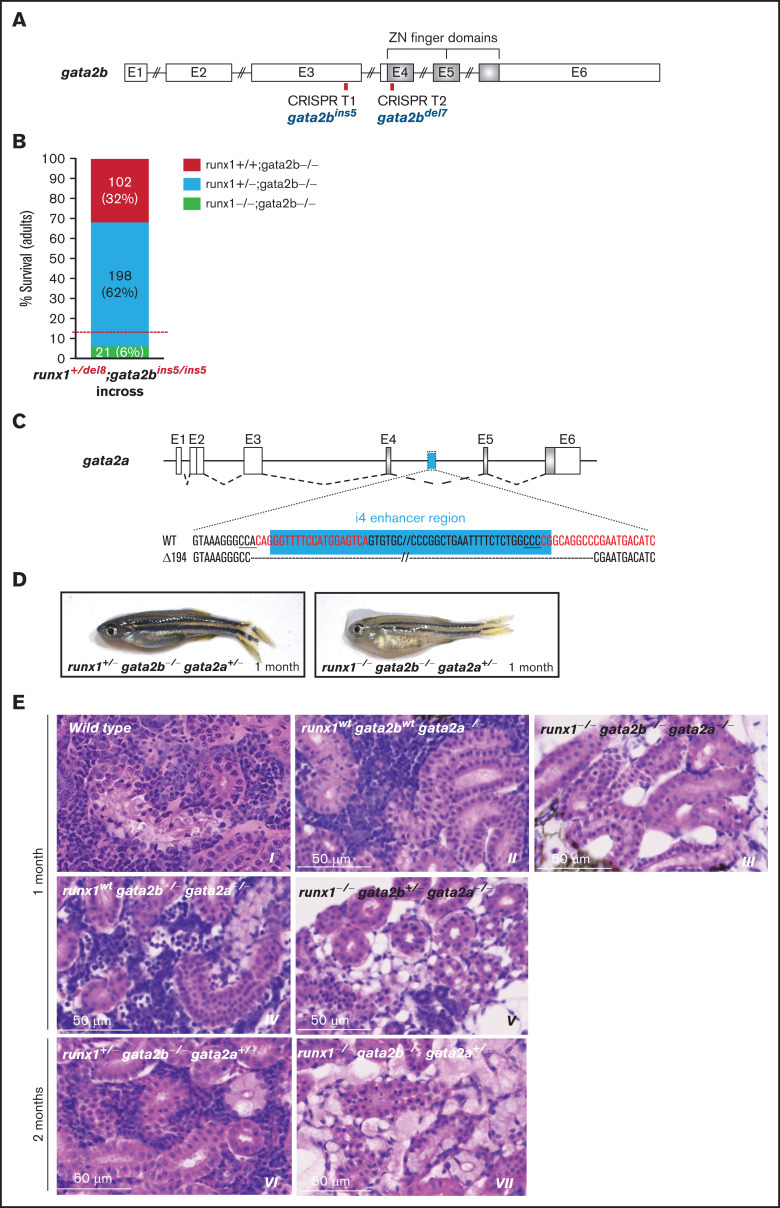
Figure 6.
gata2b and gata2a are required for the development of definitive hematopoiesis in runx1 mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the gata2b gene showing the CRISPR targets T1 and T2 (red bars) used to generate the gata2bins5 and the gata2bdel7 mutant lines. (B) Survival of adult runx1del8/gata2bins5 double mutants obtained from the incross of runx1+/del8; gata2bins5/ins5 fish. Red dashed lines indicate the expected ratio of runx1−un recovery based on our previous experimental data (Figure 1E). Each bar segment shows the percentage and number of fish recovered for each genotype. (C) Schematic representation of gata2a genomic structure. The cyan box represents the 150-bp i4 enhancer that was removed using 2 CRISPR guides (red letters). (D) Photographs of representative 1-month-old runx1+/−gata2b−atgata2a+/− and runx1−ungata2b−atgata2a−at fish, with the latter more pale and smaller than the former. (E) Histologic analysis of kidney marrow of triple mutants runx1del8;gata2bins5;gata2ai4del1 at 1 or 2 months. Kidneys from runx1 wild-type and runx1+/− fish (panels II, IV, and VI) are similar to the kidney from the wild-type control (panel I) with marrows populated by blood progenitors. Kidneys from runx1del8/del8 fish with gata2b−atgata2a−at (III), gata2b+/−gata2a−at (V), or gata2b+/−gata2a+/− (VII) completely lack blood progenitors. See supplemental Figure 7 for additional characterizations of the zebrafish gata2b and gata2a mutants.