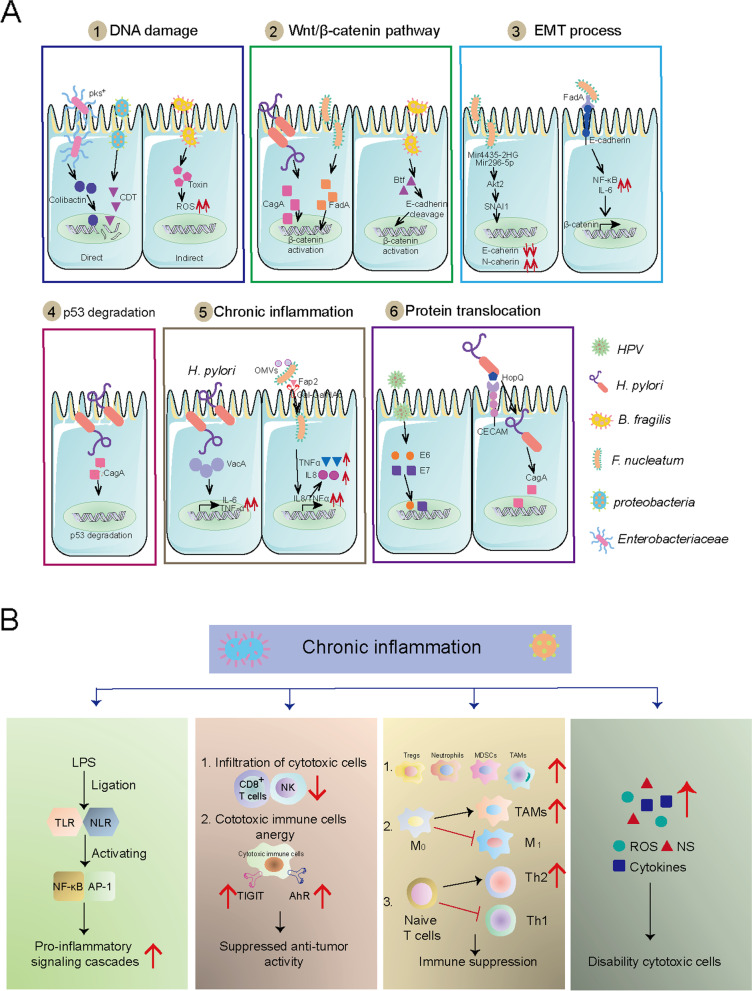
Fig. 2.
Potential molecular mechanisms by which intratumor microbiota promote carcinogenesis. A. Microbiome contributed to the tumorigenesis through inducing DNA damage, Wnt/β-catenin pathway, EMT process, p53 degradation, chronic inflammation and protein translocation. B. The chronic inflammation that induced by intratumor microbiota include cancer-associated inflammation, cancer-associated cytokines and ROS/NS production, inhibited cytotoxic immune cells infiltration and function and enhanced immunosuppressive cells infiltration and polarization