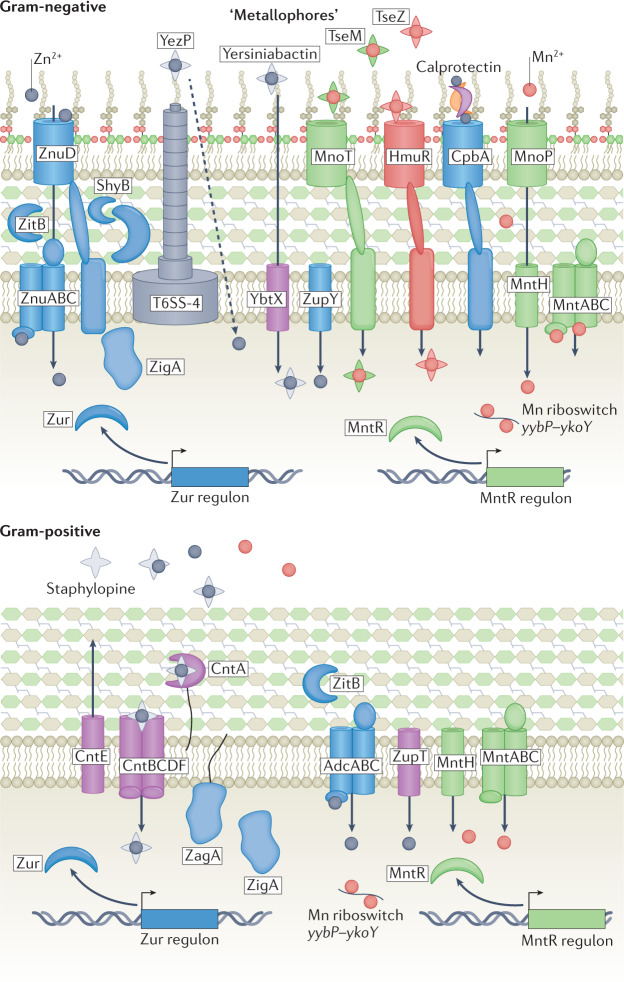
Fig. 4. Bacterial acquisition of Zn and Mn.
Pathogenic bacteria acquire zinc (Zn) using ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters ZnuABC (Gram-negative bacteria) and AdcABC (Gram-positive bacteria). Zn is transported through outer membrane using TonB-dependent transporter ZnuD in Gram-negative bacteria and ZupT in Gram-positive bacteria. Additional Zn acquisition systems include type 6 secretion system (T6SS)-secreted zincophore protein YezP in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, transport of yersiniabactin–Zn in Yersinia pestis by TonB-dependent transporter MnoT, TseZ and TseM in Burkholderia thailandensis and outer membrane receptor CbpA that binds calprotectin in Neisseria meningitidis. Manganese (Mn) is taken up by outer membrane pore MnoP in Gram-negative bacteria and imported into cytosol by MntABC or MntH transporters. In Gram-positive bacteria, Mn is transported across cell membrane by MntH or MntABC transporters. The yybP–ykoY riboswitch family binds Mn with high affinity and modulates Mn homeostasis in bacterial pathogens including Neisseria and Streptococcus spp.