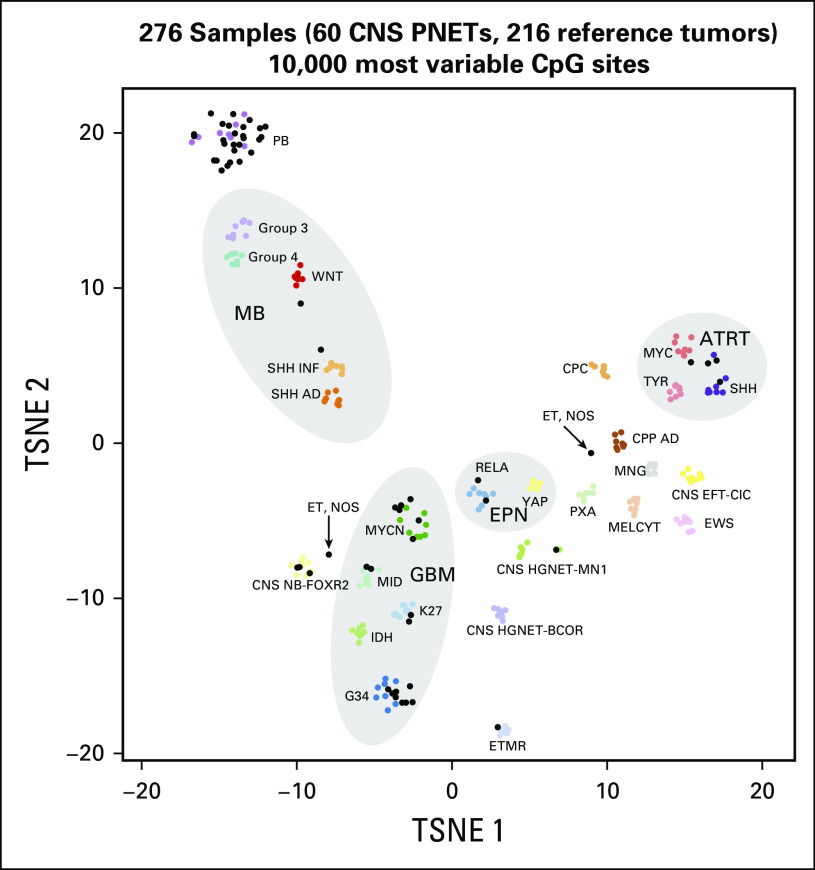
Fig 1.
Methylation profiling identifies disparate molecular diagnoses in tumors pathologically classified institutionally as supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the CNS (CNS-PNET) and pineoblastoma (PBL). Tumors were molecularly classified on the basis of unsupervised cluster analyses of the 60 CNS-PNET/PBL methylation profiles, together with the methylation profiles of 216 reference cases that represented 27 distinct molecular brain tumor entities. AD, adult; ATRT, atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor; BCOR, bcl6 corepressor; CNS EFT-CIC, Ewing sarcoma family tumor with CIC alteration; CIC, capicua transcriptional repressor; CNS NB-FOXR2, forkhead box R2; CPC, choroid plexus carcinoma; CPP, choroid plexus papilloma; EPN, ependymoma: ET, embryonal tumor; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme; HGNET-MN1, high-grade neuroepithelial tumor with MN1 alteration; INF, infant; MB, medulloblastoma; MELCYT, melanocytoma; MNG, meningioma; NOS, not otherwise specified; PB, pineoblastoma; PXA, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; RELA, v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A; SHH, Sonic Hedgehog; TSNE, stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) method; WNT, Wingless; YAP, yes-associated protein 1.