Figure 3. Multipronged effect of pharmacological targeting of PI5P4Ks in the fight against cancer.
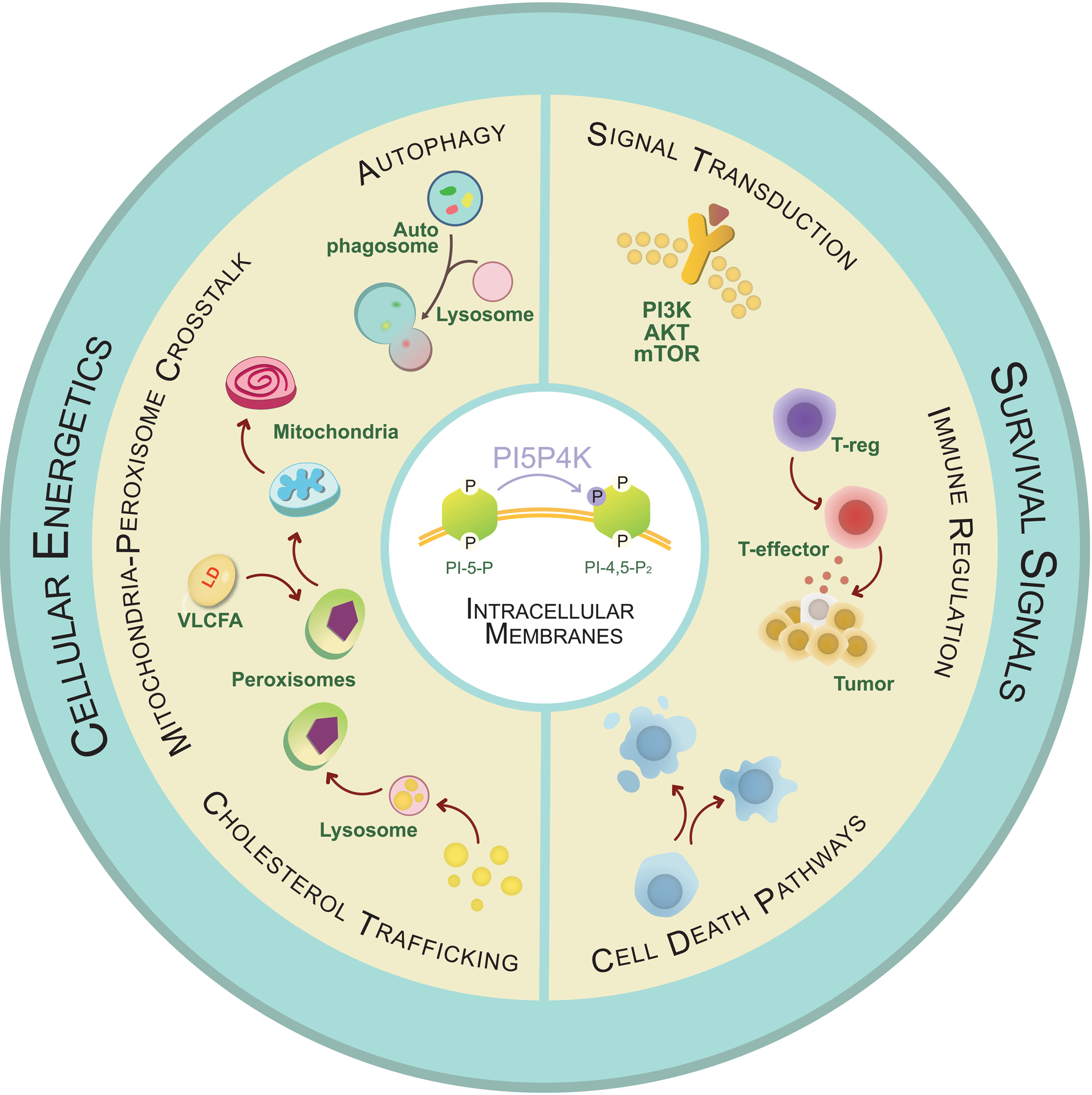
PI5P4Ks perform a central role in influencing multiple cancer hallmarks due to its dual role in cell intrinsic pathways as well as in modulation of the immune environment. PI5P4Ks contribute to the classic hallmark of evading cell-death pathways since targeting them selectively decreases survival of cancer cells. PI5P4Ks potentially regulates specialized phosphoinositide pools in subcellular organelles and modulates the dynamic contacts between organelles, exerting a far-reaching impact on cellular energetics as demonstrated by disruption of autophagy, cholesterol trafficking, ROS homeostasis and efficient peroxisomal-mitochondrial cross talk with the manipulation of the kinases. Several of the above-described functional implications arise as a result of alteration in signaling of mTOR, PI3K-Akt and AMPK networks, all of which have been crucial clinical targets for cancer treatment modalities. PI5P4Ks extend their relevance in tumor biology beyond the boundaries of the cells and into the microenvironment by selectively affecting the activity of the Tregs, allowing for the PI5P4K inhibitors to act as a combination of chemo- and immunotherapy.
