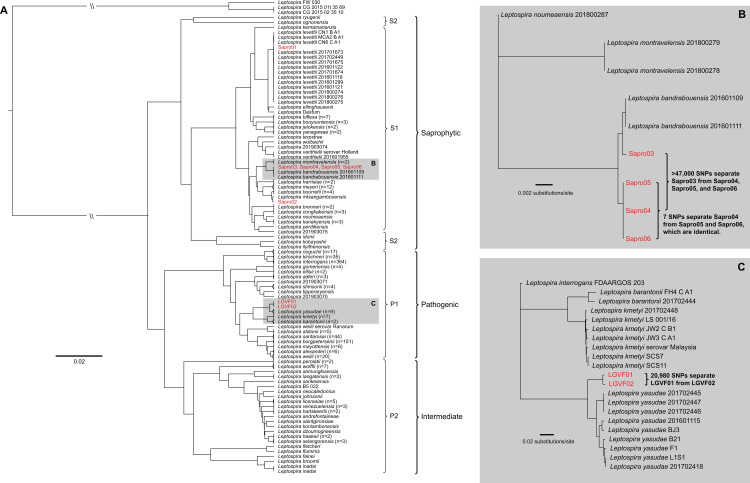
Fig 4. Whole genome dendrogram of 802 known pathogenic, intermediate, and saprophytic Leptospira spp. isolates, including six saprophytic and two pathogenic isolates obtained in this study from a single soil sample from site 16.
A) Pairwise genomic distance dendrogram contextualizing the relationship among all known saprophytic (S1 and S2), intermediate (P2), and pathogenic (P1) Leptospira spp. reveals the pathogenic isolates LGVF01 and LGVF02 represent two genotypes of the same previously undescribed pathogenic species, whereas the saprophytes belong to three known Leptospira spp. B) Detailed view of the S1 clade that contains four saprophytic isolates obtained during this study. This maximum likelihood phylogeny reveals significant diversity among isolates that fall within the L. bandrabouensis clade. C) Detailed view of the P1 clade that contains two pathogenic isolates obtained during this study. This maximum likelihood phylogeny reveals two genotypes of a novel pathogenic Leptospira spp. isolated from soil in Puerto Rico.